Generate and return the expression dot_product(x, y) accurately (almost without roundoff error).
- Parameters
-
| [in] | x | : The input contiguous vector of arbitrary size, of
-
type
complex of kind any supported by the processor (e.g., CK, CK32, CK64, or CK128), or
-
type
real of kind any supported by the processor (e.g., RK, RK32, RK64, or RK128),
representing the x value whose dot product with y is to be returned.
|
| [in] | y | : The input contiguous vector of the same size, type, and kind as the input x, of
representing the y values whose dot product with x is to be returned.
|
| [in] | method | : The input scalar object that can be,
-
the constant iteration or equivalently, an object of type iteration_type.
Specifying this option forces the use of normal iterative approach to summing all array elements.
This option is equivalent to the default implementations of the Fortran intrinsic sum().
This approach is the fastest serial method among all, but also generally the least accurate.
-
the constant recursion or equivalently, an object of type recursion_type.
Specifying this option forces the use of recursive pairwise approach to summing all array elements.
-
the constant kahanbabu or equivalently, an object of type kahanbabu_type.
Specifying this option forces the use of the Kahan-Babuska compensated approach to summing all array elements.
This algorithm, while accurate, can be up to 2-4 times more expensive than the iterative approach discussed above.
-
the constant fablocked or equivalently, an object of type fablocked_type.
Specifying this option forces the use of the Fast Accurate Blocked approach to summing all array elements.
-
the constant nablocked or equivalently, an object of type nablocked_type.
Specifying this option forces the use of the Naive Blocked approach to summing all array elements.
The presence of this argument is merely for compile-time resolution of the procedures of this generic interface.
(optional, default = fablocked.) |
- Returns
dotres : The output scalar of the same type and kind containing the result of the dot product of the input x and y vectors.
Possible calling interfaces ⛓
Generate and return the expression dot_product(x, y) accurately (almost without roundoff error).
This module contains procedures and generic interfaces for computing sum(x) accurately when x is a lo...
type(kahanbabu_type), parameter kahanbabu
This is a scalar parameter object of type kahanbabu_type.
type(fablocked_type), parameter fablocked
This is a scalar parameter object of type fablocked_type.
type(nablocked_type), parameter nablocked
This is a scalar parameter object of type nablocked_type.
- Warning
- The returned value is
0 is the size of the condition size(x) == 0 holds.
The condition size(x) == size(y) must hold for the corresponding input arguments.
This condition is verified only if the library is built with the preprocessor macro CHECK_ENABLED=1.
-
The
pure procedure(s) documented herein become impure when the ParaMonte library is compiled with preprocessor macro CHECK_ENABLED=1.
By default, these procedures are pure in release build and impure in debug and testing builds.
- See also
- get1mexp
getLog1p
getCumSum
getLogAddExp
getLogSubExp
getLogSumExp
Example usage ⛓
13 real(RKH),
allocatable :: dotres(:), relerr(:)
14 type(display_type) :: disp
20 integer(IK),
parameter :: lenx
= 10**7
21 real(TKG) :: x(lenx), y(lenx), lb, ub
25 call disp%show(
"lb = real(lenx, TKG); ub = 1._TKG")
26 lb
= real(lenx, TKG); ub
= 1._TKG
27 call disp%show(
"call setLinSpace(x, lb, ub) ! call setUnifRand(x)")
31 call disp%show(
"truth = (real(ub, TKG) + real(lb, RKH)) * size(x, 1, IK) / 2 ! reference high-precision value for comparison")
32 truth
= (
real(ub, TKG)
+ real(lb,
RKH))
* size(x,
1,
IK)
/ 2
35 call disp%show(
"dotres = [getDot(x, y), getDot(x, y, iteration), getDot(x, y, recursion), getDot(x, y, kahanbabu), getDot(x, y, fablocked), getDot(x, y, nablocked)]")
36 dotres
= [
getDot(x, y),
getDot(x, y, iteration),
getDot(x, y, recursion),
getDot(x, y,
kahanbabu),
getDot(x, y,
fablocked),
getDot(x, y,
nablocked)]
39 call disp%show(
"relerr = abs(truth - dotres) / truth")
40 relerr
= abs(truth
- dotres)
/ truth
43 call disp%show(
"getRankDense(relerr)")
50 integer(IK),
parameter :: lenx
= 10**8
51 real(TKG) :: x(lenx), y(lenx), lb, ub
55 call disp%show(
"lb = real(lenx, TKG); ub = 1._TKG")
56 lb
= real(lenx, TKG); ub
= 1._TKG
57 call disp%show(
"call setLinSpace(x, lb, ub) ! call setUnifRand(x)")
61 call disp%show(
"truth = (real(ub, TKG) + real(lb, RKH)) * size(x, 1, IK) / 2 ! reference high-precision value for comparison")
62 truth
= (
real(ub, TKG)
+ real(lb,
RKH))
* size(x,
1,
IK)
/ 2
65 call disp%show(
"dotres = [getDot(x, y), getDot(x, y, iteration), getDot(x, y, recursion), getDot(x, y, kahanbabu), getDot(x, y, fablocked), getDot(x, y, nablocked)]")
66 dotres
= [
getDot(x, y),
getDot(x, y, iteration),
getDot(x, y, recursion),
getDot(x, y,
kahanbabu),
getDot(x, y,
fablocked),
getDot(x, y,
nablocked)]
69 call disp%show(
"relerr = abs(truth - dotres) / truth")
70 relerr
= abs(truth
- dotres)
/ truth
73 call disp%show(
"getRankDense(relerr)")
80 call disp%show(
"[getDot([real ::], [real ::]), getDot([real :: 1], [real :: 1]), getDot([real :: 1, 1], [real :: 1, 1]), getDot([real :: 1, 1, 1], [real :: 1, 1, 1])]")
81 call disp%show( [
getDot([real ::], [real ::]),
getDot([real ::
1], [real ::
1]),
getDot([real ::
1,
1], [real ::
1,
1]),
getDot([real ::
1,
1,
1], [real ::
1,
1,
1])] )
Generate and return the Dense rank of the input scalar string or contiguous array of rank 1 in ascend...
Return the linSpace output argument with size(linSpace) elements of evenly-spaced values over the int...
Return a uniform random scalar or contiguous array of arbitrary rank of randomly uniformly distribute...
This is a generic method of the derived type display_type with pass attribute.
This is a generic method of the derived type display_type with pass attribute.
This module contains procedures and generic interfaces for obtaining various rankings of elements of ...
This module contains procedures and generic interfaces for generating arrays with linear or logarithm...
This module contains classes and procedures for computing various statistical quantities related to t...
This module contains classes and procedures for input/output (IO) or generic display operations on st...
type(display_type) disp
This is a scalar module variable an object of type display_type for general display.
This module defines the relevant Fortran kind type-parameters frequently used in the ParaMonte librar...
integer, parameter LK
The default logical kind in the ParaMonte library: kind(.true.) in Fortran, kind(....
integer, parameter IK
The default integer kind in the ParaMonte library: int32 in Fortran, c_int32_t in C-Fortran Interoper...
integer, parameter RKD
The double precision real kind in Fortran mode. On most platforms, this is an 64-bit real kind.
integer, parameter SK
The default character kind in the ParaMonte library: kind("a") in Fortran, c_char in C-Fortran Intero...
integer, parameter RKH
The scalar integer constant of intrinsic default kind, representing the highest-precision real kind t...
integer, parameter RKS
The single-precision real kind in Fortran mode. On most platforms, this is an 32-bit real kind.
Generate and return an object of type display_type.
Example Unix compile command via Intel ifort compiler ⛓
3ifort -fpp -standard-semantics -O3 -Wl,-rpath,../../../lib -I../../../inc main.F90 ../../../lib/libparamonte* -o main.exe
Example Windows Batch compile command via Intel ifort compiler ⛓
2set PATH=..\..\..\lib;%PATH%
3ifort /fpp /standard-semantics /O3 /I:..\..\..\include main.F90 ..\..\..\lib\libparamonte*.lib /exe:main.exe
Example Unix / MinGW compile command via GNU gfortran compiler ⛓
3gfortran -cpp -ffree-line-length-none -O3 -Wl,-rpath,../../../lib -I../../../inc main.F90 ../../../lib/libparamonte* -o main.exe
Example output ⛓
4lb
= real(lenx, TKG); ub
= 1._TKG
7truth
= (
real(ub, TKG)
+ real(lb,
RKH))
* size(x,
1,
IK)
/ 2
9+50000005000000.0000000000000000000000
10dotres
= [
getDot(x, y),
getDot(x, y, iteration),
getDot(x, y, recursion),
getDot(x, y,
kahanbabu),
getDot(x, y,
fablocked),
getDot(x, y,
nablocked)]
12+50000000188416.0000000000000000000000,
+49423623127040.0000000000000000000000,
+50000008577024.0000000000000000000000,
+50000004382720.0000000000000000000000,
+50000000188416.0000000000000000000000,
+49999983411200.0000000000000000000000
13relerr
= abs(truth
- dotres)
/ truth
15+0.962316703768329623167037683296231645E-7,
+0.115276363064363693563630643636935635E-1,
+0.715404728459527154047284595271540462E-7,
+0.123455987654401234559876544012345606E-7,
+0.962316703768329623167037683296231645E-7,
+0.431775956822404317759568224043177598E-6
22lb
= real(lenx, TKG); ub
= 1._TKG
25truth
= (
real(ub, TKG)
+ real(lb,
RKH))
* size(x,
1,
IK)
/ 2
27+5000000050000000.00000000000000000000
28dotres
= [
getDot(x, y),
getDot(x, y, iteration),
getDot(x, y, recursion),
getDot(x, y,
kahanbabu),
getDot(x, y,
fablocked),
getDot(x, y,
nablocked)]
30+5000000050000000.00000000000000000000,
+5000000050000000.00000000000000000000,
+5000000050000000.00000000000000000000,
+5000000050000000.00000000000000000000,
+5000000050000000.00000000000000000000,
+5000000050000000.00000000000000000000
31relerr
= abs(truth
- dotres)
/ truth
33+0.00000000000000000000000000000000000,
+0.00000000000000000000000000000000000,
+0.00000000000000000000000000000000000,
+0.00000000000000000000000000000000000,
+0.00000000000000000000000000000000000,
+0.00000000000000000000000000000000000
38[
getDot([real ::], [real ::]),
getDot([real ::
1], [real ::
1]),
getDot([real ::
1,
1], [real ::
1,
1]),
getDot([real ::
1,
1,
1], [real ::
1,
1,
1])]
39+0.00000000,
+1.00000000,
+2.00000000,
+3.00000000
- Benchmarks:
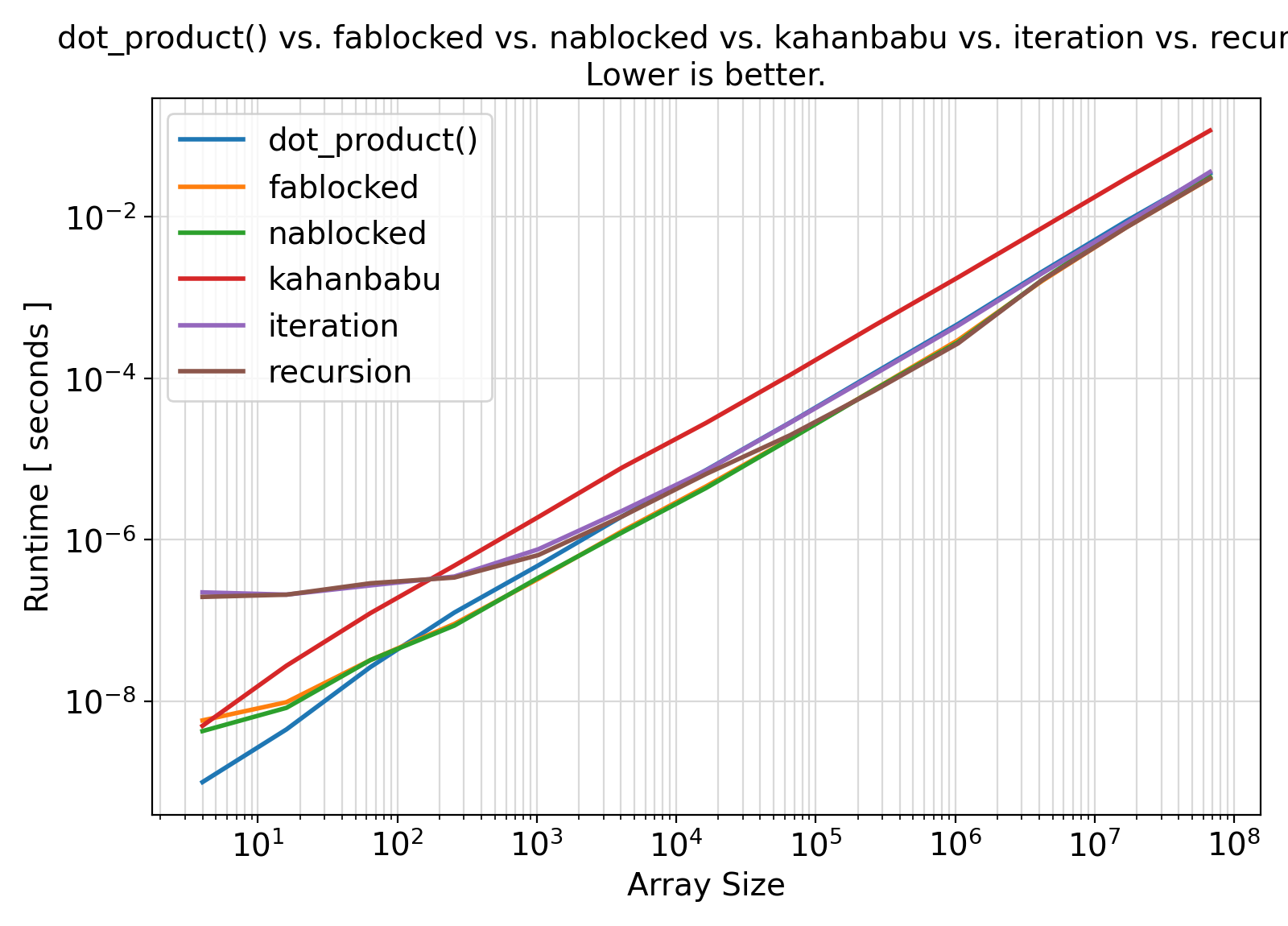
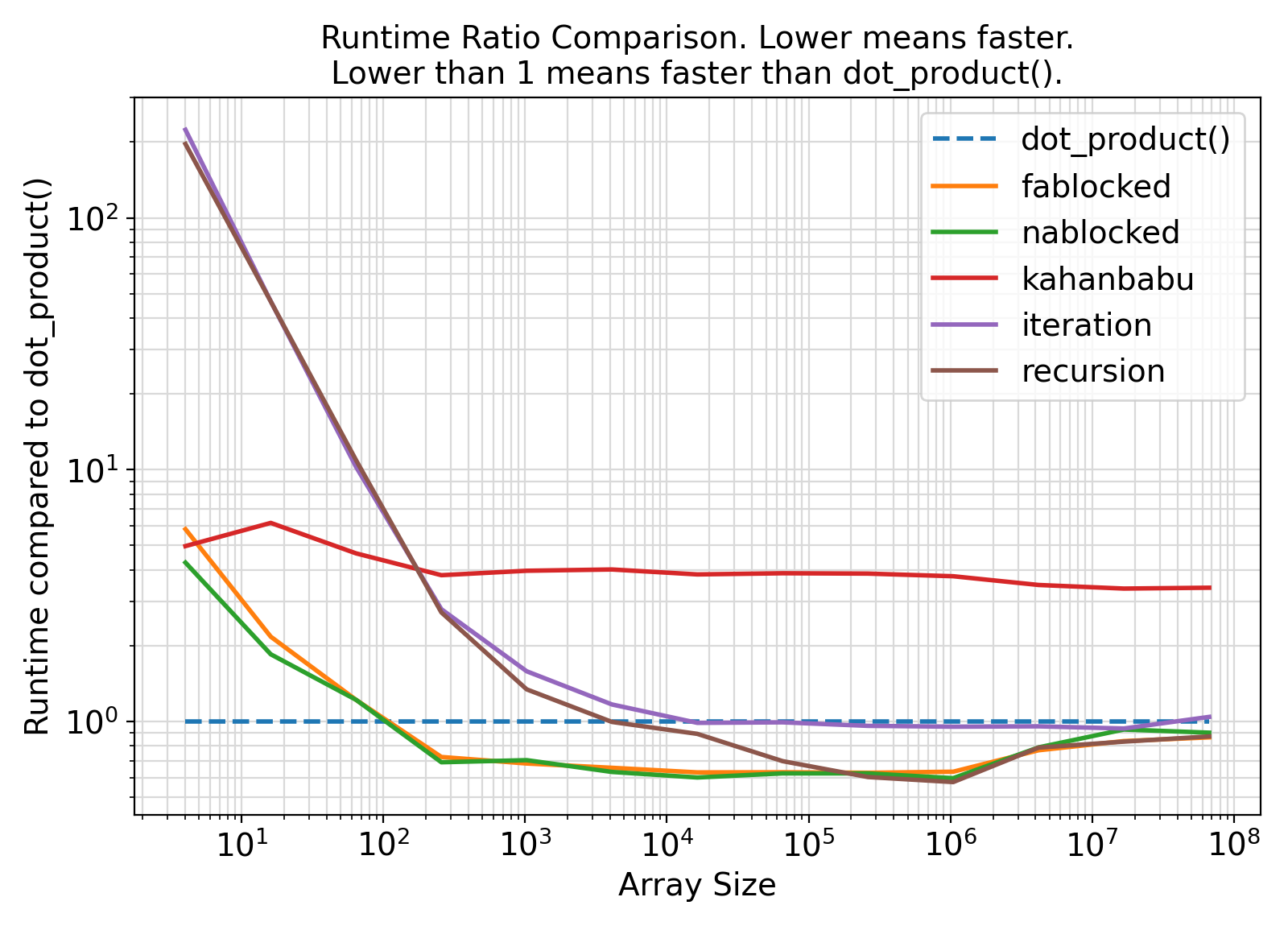
Benchmark :: The effects of method on runtime efficiency ⛓
- The following program compares the runtime performance of getDot algorithms with the default Fortran
dot_product() intrinsic function.
9 use iso_fortran_env,
only:
error_unit
16 integer(IK) :: fileUnit
17 real(RKG) :: dumsum
= 0._RKG
18 real(RKG) :: array(
10**8)
20 type(bench_type) ,
allocatable :: bench(:)
21 logical(LK) :: underflowEnabled
23 bench
= [
bench_type(name
= SK_
"dot_product()", exec
= getDotFortran, overhead
= setOverhead)
&
24 ,
bench_type(name
= SK_
"fablocked", exec
= getDotFAB, overhead
= setOverhead)
&
25 ,
bench_type(name
= SK_
"nablocked", exec
= getDotNAB, overhead
= setOverhead)
&
26 ,
bench_type(name
= SK_
"kahanbabu", exec
= getDotKAB, overhead
= setOverhead)
&
27 ,
bench_type(name
= SK_
"iteration", exec
= getDotIte, overhead
= setOverhead)
&
28 ,
bench_type(name
= SK_
"recursion", exec
= getDotRec, overhead
= setOverhead)
&
31 write(
*,
"(*(g0,:,' '))")
32 write(
*,
"(*(g0,:,' '))")
"dot_product() vs. getDot()"
33 write(
*,
"(*(g0,:,' '))")
35 open(newunit
= fileUnit, file
= "main.out", status
= "replace")
39 write(fileUnit,
"(*(g0,:,','))")
"Array Size", (bench(ibench)
%name, ibench
= 1,
size(bench))
40 loopOverArraySize:
do iarr
= 2,
26,
2
43 write(
*,
"(*(g0,:,' '))")
"Benchmarking with array size", arrlen
44 do ibench
= 1,
size(bench)
45 bench(ibench)
%timing
= bench(ibench)
%getTiming(minsec
= 0.07_RK)
47 write(fileUnit,
"(*(g0,:,','))") arrlen, (bench(ibench)
%timing
%mean, ibench
= 1,
size(bench))
49 end do loopOverArraySize
50 write(
*,
"(*(g0,:,' '))") dumsum
51 write(
*,
"(*(g0,:,' '))")
61 subroutine setOverhead()
66 dumsum
= dumsum
+ dotres
69 subroutine getDotFortran()
70 dotres
= dot_product(array(
1 : arrlen), array(
1 : arrlen))
74 subroutine getDotFAB()
76 dotres
= getDot(array(
1 : arrlen), array(
1 : arrlen))
80 subroutine getDotNAB()
86 subroutine getDotKAB()
92 subroutine getDotIte()
94 dotres
= getDot(array(
1 : arrlen), array(
1 : arrlen), iteration)
98 subroutine getDotRec()
100 dotres
= getDot(array(
1 : arrlen), array(
1 : arrlen), recursion)
Allocate or resize (shrink or expand) an input allocatable scalar string or array of rank 1....
Generate and return an object of type timing_type containing the benchmark timing information and sta...
Return the cumulative sum of the input array, optionally in the backward direction and optionally,...
This module contains procedures and generic interfaces for resizing allocatable arrays of various typ...
This module contains abstract interfaces and types that facilitate benchmarking of different procedur...
integer, parameter RK
The default real kind in the ParaMonte library: real64 in Fortran, c_double in C-Fortran Interoperati...
This module contains the procedures and interfaces for computing the cumulative sum of an array.
This is the class for creating benchmark and performance-profiling objects.
Example Unix compile command via Intel ifort compiler ⛓
3ifort -fpp -standard-semantics -O3 -Wl,-rpath,../../../lib -I../../../inc main.F90 ../../../lib/libparamonte* -o main.exe
Example Windows Batch compile command via Intel ifort compiler ⛓
2set PATH=..\..\..\lib;%PATH%
3ifort /fpp /standard-semantics /O3 /I:..\..\..\include main.F90 ..\..\..\lib\libparamonte*.lib /exe:main.exe
Example Unix / MinGW compile command via GNU gfortran compiler ⛓
3gfortran -cpp -ffree-line-length-none -O3 -Wl,-rpath,../../../lib -I../../../inc main.F90 ../../../lib/libparamonte* -o main.exe
Postprocessing of the benchmark output ⛓
3import matplotlib.pyplot
as plt
8dirname = os.path.basename(os.getcwd())
12df = pd.read_csv(
"main.out", delimiter =
",")
13colnames = list(df.columns.values)
19ax = plt.figure(figsize = 1.25 * np.array([6.4,4.6]), dpi = 200)
22for colname
in colnames[1:]:
23 plt.plot( df[colnames[0]].values
28plt.xticks(fontsize = fontsize)
29plt.yticks(fontsize = fontsize)
30ax.set_xlabel(colnames[0], fontsize = fontsize)
31ax.set_ylabel(
"Runtime [ seconds ]", fontsize = fontsize)
32ax.set_title(
" vs. ".join(colnames[1:])+
"\nLower is better.", fontsize = fontsize)
36plt.grid(visible =
True, which =
"both", axis =
"both", color =
"0.85", linestyle =
"-")
37ax.tick_params(axis =
"y", which =
"minor")
38ax.tick_params(axis =
"x", which =
"minor")
39ax.legend ( colnames[1:]
46plt.savefig(
"benchmark." + dirname +
".runtime.png")
52ax = plt.figure(figsize = 1.25 * np.array([6.4,4.6]), dpi = 200)
55plt.plot( df[colnames[0]].values
56 , np.ones(len(df[colnames[0]].values))
61for colname
in colnames[2:]:
62 plt.plot( df[colnames[0]].values
63 , df[colname].values / df[colnames[1]].values
67plt.xticks(fontsize = fontsize)
68plt.yticks(fontsize = fontsize)
69ax.set_xlabel(colnames[0], fontsize = fontsize)
70ax.set_ylabel(
"Runtime compared to {}".format(colnames[1]), fontsize = fontsize)
71ax.set_title(
"Runtime Ratio Comparison. Lower means faster.\nLower than 1 means faster than {}.".format(colnames[1]), fontsize = fontsize)
75plt.grid(visible =
True, which =
"both", axis =
"both", color =
"0.85", linestyle =
"-")
76ax.tick_params(axis =
"y", which =
"minor")
77ax.tick_params(axis =
"x", which =
"minor")
78ax.legend ( colnames[1:]
85plt.savefig(
"benchmark." + dirname +
".runtime.ratio.png")
Visualization of the benchmark output ⛓
Benchmark moral ⛓
- Among all summation algorithms, fablocked_type appears to offer the most accurate result while also being even faster than the default Fortran
dot_product() and all other implemented summation algorithms for array sizes > 100.
- Test:
- test_pm_mathSum
Final Remarks ⛓
If you believe this algorithm or its documentation can be improved, we appreciate your contribution and help to edit this page's documentation and source file on GitHub.
For details on the naming abbreviations, see this page.
For details on the naming conventions, see this page.
This software is distributed under the MIT license with additional terms outlined below.
-
If you use any parts or concepts from this library to any extent, please acknowledge the usage by citing the relevant publications of the ParaMonte library.
-
If you regenerate any parts/ideas from this library in a programming environment other than those currently supported by this ParaMonte library (i.e., other than C, C++, Fortran, MATLAB, Python, R), please also ask the end users to cite this original ParaMonte library.
This software is available to the public under a highly permissive license.
Help us justify its continued development and maintenance by acknowledging its benefit to society, distributing it, and contributing to it.
- Copyright
- Computational Data Science Lab
- Author:
- Amir Shahmoradi, August 8, 2024, 10:23 PM, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Washington, D.C.
Definition at line 1247 of file pm_mathSum.F90.