This module contains the procedures and interfaces for computing the cumulative sum of an array.
More...
This module contains the procedures and interfaces for computing the cumulative sum of an array.
- Benchmarks:
Benchmark :: The runtime performance of getCumSum vs. setCumSum ⛓
4 use iso_fortran_env,
only:
error_unit
12 integer(IK) :: fileUnit
13 integer(IK) ,
parameter :: NARR
= 11_IK
14 integer(IK) :: arraySize(NARR)
15 real(RK) :: dummySum
= 0._RK
16 real(RK) ,
allocatable :: array(:)
17 real(RK) ,
allocatable :: cumsum(:)
18 type(bench_type),
allocatable :: bench(:)
20 bench
= [
bench_type(name
= SK_
"setCumSum", exec
= setCumSum, overhead
= setOverhead)
&
21 ,
bench_type(name
= SK_
"getCumSum", exec
= getCumSum, overhead
= setOverhead)
&
22 ,
bench_type(name
= SK_
"setCumSum_overwrite", exec
= setCumSum_overwrite, overhead
= setOverhead)
&
23 ,
bench_type(name
= SK_
"getCumSum_withBounds", exec
= getCumSum_withBounds, overhead
= setOverhead)
&
26 arraySize
= [(
2_IK**iarr, iarr
= 1_IK, NARR )]
28 write(
*,
"(*(g0,:,' '))")
29 write(
*,
"(*(g0,:,' '))")
"setCumSum() vs. getCumSum() vs. getCumSum_withBounds()"
30 write(
*,
"(*(g0,:,' '))")
32 open(newunit
= fileUnit, file
= "main.out", status
= "replace")
34 write(fileUnit,
"(*(g0,:,','))")
"arraySize", (bench(i)
%name, i
= 1,
size(bench))
36 loopOverArraySize:
do iarr
= 1, NARR
38 allocate(array(arraySize(iarr)))
39 allocate(cumsum(arraySize(iarr)),
source = 0._RK)
40 write(
*,
"(*(g0,:,' '))")
"Benchmarking with array size", arraySize(iarr)
45 write(fileUnit,
"(*(g0,:,','))") arraySize(iarr), (bench(i)
%timing
%mean, i
= 1,
size(bench))
47 deallocate(array, cumsum)
49 end do loopOverArraySize
50 write(
*,
"(*(g0,:,' '))") dummySum
51 write(
*,
"(*(g0,:,' '))")
61 subroutine setOverhead()
67 call random_number(array)
71 dummySum
= dummySum
+ cumsum(
1)
+ array(
1)
74 subroutine setCumSum()
83 subroutine setCumSum_overwrite()
92 subroutine getCumSum()
101 subroutine getCumSum_withBounds()
Generate and return an object of type timing_type containing the benchmark timing information and sta...
Generate and return the cumulative sum of the input array, optionally in the backward direction and,...
Return the cumulative sum of the input array, optionally in the backward direction and optionally,...
This module contains abstract interfaces and types that facilitate benchmarking of different procedur...
This module defines the relevant Fortran kind type-parameters frequently used in the ParaMonte librar...
integer, parameter RK
The default real kind in the ParaMonte library: real64 in Fortran, c_double in C-Fortran Interoperati...
integer, parameter IK
The default integer kind in the ParaMonte library: int32 in Fortran, c_int32_t in C-Fortran Interoper...
integer, parameter SK
The default character kind in the ParaMonte library: kind("a") in Fortran, c_char in C-Fortran Intero...
This module contains the procedures and interfaces for computing the cumulative sum of an array.
This is the class for creating benchmark and performance-profiling objects.
Example Unix compile command via Intel ifort compiler ⛓
3ifort -fpp -standard-semantics -O3 -Wl,-rpath,../../../lib -I../../../inc main.F90 ../../../lib/libparamonte* -o main.exe
Example Windows Batch compile command via Intel ifort compiler ⛓
2set PATH=..\..\..\lib;%PATH%
3ifort /fpp /standard-semantics /O3 /I:..\..\..\include main.F90 ..\..\..\lib\libparamonte*.lib /exe:main.exe
Example Unix / MinGW compile command via GNU gfortran compiler ⛓
3gfortran -cpp -ffree-line-length-none -O3 -Wl,-rpath,../../../lib -I../../../inc main.F90 ../../../lib/libparamonte* -o main.exe
Postprocessing of the benchmark output ⛓
3import matplotlib.pyplot
as plt
8dirname = os.path.basename(os.getcwd())
12df = pd.read_csv(
"main.out", delimiter =
",")
13colnames = list(df.columns.values)
19ax = plt.figure(figsize = 1.25 * np.array([6.4,4.6]), dpi = 200)
22for colname
in colnames[1:]:
23 plt.plot( df[colnames[0]].values
28plt.xticks(fontsize = fontsize)
29plt.yticks(fontsize = fontsize)
30ax.set_xlabel(colnames[0], fontsize = fontsize)
31ax.set_ylabel(
"Runtime [ seconds ]", fontsize = fontsize)
32ax.set_title(
" vs. ".join(colnames[1:])+
"\nLower is better.", fontsize = fontsize)
36plt.grid(visible =
True, which =
"both", axis =
"both", color =
"0.85", linestyle =
"-")
37ax.tick_params(axis =
"y", which =
"minor")
38ax.tick_params(axis =
"x", which =
"minor")
39ax.legend ( colnames[1:]
46plt.savefig(
"benchmark." + dirname +
".runtime.png")
52ax = plt.figure(figsize = 1.25 * np.array([6.4,4.6]), dpi = 200)
55plt.plot( df[colnames[0]].values
56 , np.ones(len(df[colnames[0]].values))
61for colname
in colnames[2:]:
62 plt.plot( df[colnames[0]].values
63 , df[colname].values / df[colnames[1]].values
67plt.xticks(fontsize = fontsize)
68plt.yticks(fontsize = fontsize)
69ax.set_xlabel(colnames[0], fontsize = fontsize)
70ax.set_ylabel(
"Runtime compared to {}".format(colnames[1]), fontsize = fontsize)
71ax.set_title(
"Runtime Ratio Comparison. Lower means faster.\nLower than 1 means faster than {}().".format(colnames[1]), fontsize = fontsize)
75plt.grid(visible =
True, which =
"both", axis =
"both", color =
"0.85", linestyle =
"-")
76ax.tick_params(axis =
"y", which =
"minor")
77ax.tick_params(axis =
"x", which =
"minor")
78ax.legend ( colnames[1:]
85plt.savefig(
"benchmark." + dirname +
".runtime.ratio.png")
Visualization of the benchmark output ⛓
Benchmark moral ⛓
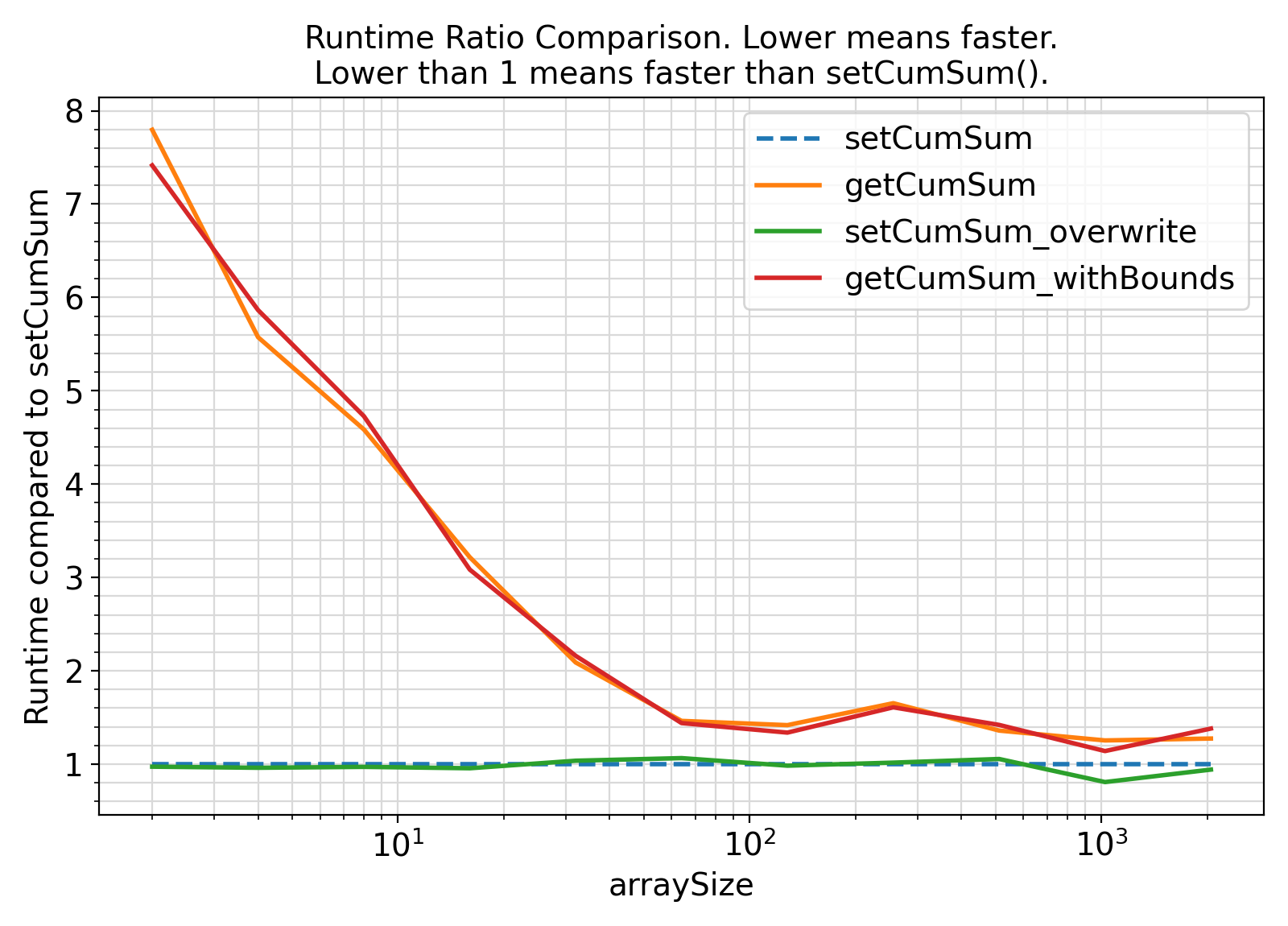
- The procedures under the generic interface getCumSum are functions while the procedures under the generic interface setCumSum are subroutines.
From the benchmark results, it appears that the functional interface performs less efficiently than the subroutine interface.
- Furthermore, specifying the array bounds on the left-hand-side (LHS) assignment in the case of the functional interface (to avoid automatic reallocation) does not appear to enhance the performance of the functional interface in any meaningful way.
In other words, the compiler appears to be smart enough to not reallocate the LHS needlessly.
- Test:
- test_pm_mathCumSum
Final Remarks ⛓
If you believe this algorithm or its documentation can be improved, we appreciate your contribution and help to edit this page's documentation and source file on GitHub.
For details on the naming abbreviations, see this page.
For details on the naming conventions, see this page.
This software is distributed under the MIT license with additional terms outlined below.
-
If you use any parts or concepts from this library to any extent, please acknowledge the usage by citing the relevant publications of the ParaMonte library.
-
If you regenerate any parts/ideas from this library in a programming environment other than those currently supported by this ParaMonte library (i.e., other than C, C++, Fortran, MATLAB, Python, R), please also ask the end users to cite this original ParaMonte library.
This software is available to the public under a highly permissive license.
Help us justify its continued development and maintenance by acknowledging its benefit to society, distributing it, and contributing to it.
- Copyright
- Computational Data Science Lab
- Author:
- Amir Shahmoradi, April 25, 2015, 2:21 PM, National Institute for Fusion Studies, The University of Texas Austin