Return the cumulative sum of the proportions of the exponential of the input array, optionally in the backward direction and, optionally reverse the output cumulative sum upon return.
More...
Return the cumulative sum of the proportions of the exponential of the input array, optionally in the backward direction and, optionally reverse the output cumulative sum upon return.
The returned array is normalized such that all of its elements fall in the range \([0,1]\).
All operations are performed while avoiding arithmetic overflow.
- Parameters
-
| [out] | cumPropExp | : The output array of the same size, shape, type, and kind as the input array containing the cumulative sum of proportions of array in the specified direction.
(optional, if missing, the result will be written to the input/output argument array.) |
| [in,out] | array | : The contiguous array of shape (:) of type real of kind any supported by the processor (e.g., RK, RK32, RK64, or RK128) whose cumulative proportional sum will have to be computed.
-
If
cumPropExp is present, then array has intent(in).
-
If
cumPropExp is missing, then array has intent(inout).
On output, the contents of array will be completely overwritten by the computed cumPropExp.
|
| [in] | maxArray | : The input scalar of the same type and kind as the input array representing the maximum value in array (i.e., maxArray = maxval(array)). |
| [in] | control | : The input scalar object that can be,
-
the constant sequence or equivalently, an object of type sequence_type.
Specifying this value forces the algorithm to skip runtime underflow checks.
This means all exponentiation operations will be carried out for each element.
Specifying this value can aid runtime efficiency when the divisions of none or very few of the elements of array (for example, half or less) by maxArray causes underflow.
In such cases, the potentially expensive runtime branching is avoided at the cost of performing a very few exponentiation operations.
The typical cost of an if-branch is 7-20 CPU cycles on the contemporary architecture while exponentiation typically costs ~200 CPU cycles.
See the relevant benchmark here.
-
the constant selection or equivalently, an object of type selection_type.
Enabling this option can aid runtime efficiency when the division of a significant number of elements of array (for example, half or more) by maxArray causes underflow.
In such cases, the exponentiation is avoided if control = selection` leading to faster runtime by avoiding exponentiation since it is highly expensive (on the order of ~200 CPU cycles).
See the relevant benchmark here.
|
| [in] | direction | : The input scalar object that can be,
-
the constant forward or equivalently, an object of type forward_type, implying that the output cumulative sum has be computed from the first element to the last element of the input
array.
even though the increments will still be written from the first element of cumPropExp to the last.
-
the constant backward or equivalently, an object of type backward_type, implying that the output cumulative sum has be computed from the last element to the first element of the input
array even though the increments will still be written from the first element of cumPropExp to the last.
(optional, default = sequence. It must be present if and only if the input argument action is also present.) |
| [in] | action | : The input scalar object that can be,
-
the constant nothing or equivalently, an object of type nothing_type, implying no action to be performed on the elements of the output
cumPropExp will have be reversed upon return.
-
the constant reverse or equivalently, an object of type reverse_type, implying that the order of the elements of the output
cumPropExp will have be reversed upon return, such that its last element becomes the first.
(optional, default = nothing. It must be present if and only if the input argument direction is also present.) |
Possible calling interfaces ⛓
use pm_mathCumPropExp,
only: selection, sequence, forward, backward, nothing, reverse
call setCumPropExp(array(:), maxArray, control, direction, action)
call setCumPropExp(cumPropExp(:), array(:), maxArray, control, direction, action)
Return the cumulative sum of the proportions of the exponential of the input array,...
This module contains the procedures and interfaces for computing the cumulative sum of the exponentia...
- Warning
- The condition
0 < size(array) must hold for the corresponding arguments.
The condition maxArray == maxval(array) must hold for the corresponding arguments.
The condition size(array) == size(cumPropExp) must hold for the corresponding arguments.
These conditions are verified only if the library is built with the preprocessor macro CHECK_ENABLED=1.
-
The
pure procedure(s) documented herein become impure when the ParaMonte library is compiled with preprocessor macro CHECK_ENABLED=1.
By default, these procedures are pure in release build and impure in debug and testing builds.
- Note
- The functionalities of the procedures under this generic interface,
block
call setCumPropExp(cumPropExp, array, maxArray, control, direction
= backward)
call setCumPropExp(cumPropExp, array, maxArray, control, direction
= backward,
action = reverse)
call setCumPropExp(cumPropExp, array, maxArray, control, direction
= forward,
action = reverse)
end block
!
block
cumPropExp = getCumSum(exp(array - maxval(array))); cumPropExp = cumPropExp / cumPropExp(size(array, maxArray, 1, IK))
cumPropExp = getCumSum(exp(array - maxval(array)), direction = backward); cumPropExp = cumPropExp / cumPropExp(size(array, maxArray, 1, IK))
cumPropExp = getCumSum(exp(array - maxval(array)), direction = backward, action = reversed); cumPropExp = cumPropExp / cumPropExp(1)
cumPropExp = getCumSum(exp(array - maxval(array)), direction = forward, action = reversed); cumPropExp = cumPropExp / cumPropExp(1)
end block
!
- See also
- getCumSum
setCumSum
getCumPropExp
setCumPropExp
Example usage ⛓
6 use pm_mathCumPropExp,
only: forward, backward, reverse, nothing, sequence, selection
13 type(display_type) :: disp
19 real,
allocatable :: array(:), cumPropExp(:)
21 call disp%show(
"array = log([1., 2., 3., 4.])")
22 array
= log([
1.,
2.,
3.,
4.])
25 call disp%show(
"call setResized(cumPropExp, size(array, 1, IK))")
27 call disp%show(
"call setCumPropExp(cumPropExp, array, maxval(array), sequence)")
28 call setCumPropExp(cumPropExp, array,
maxval(array), sequence)
31 call disp%show(
"call setCumPropExp(cumPropExp, array, maxval(array), selection)")
32 call setCumPropExp(cumPropExp, array,
maxval(array), selection)
36 call disp%show(
"array = array(size(array):1:-1)")
37 array
= array(
size(array):
1:
-1)
40 call disp%show(
"call setCumPropExp(cumPropExp, array, maxval(array), sequence, backward, nothing)")
41 call setCumPropExp(cumPropExp, array,
maxval(array), sequence, backward, nothing)
45 call disp%show(
"call setCumPropExp(cumPropExp, array, maxval(array), sequence, backward, reverse)")
46 call setCumPropExp(cumPropExp, array,
maxval(array), sequence, backward, reverse)
53 call disp%show(
"!%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%")
54 call disp%show(
"! Compute and return the cumulative sum in-place, within the input `Array`.")
55 call disp%show(
"!%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%")
60 real,
allocatable :: array(:)
62 call disp%show(
"array = log([1., 2., 3., 4.])")
63 array
= log([
1.,
2.,
3.,
4.])
66 call disp%show(
"call setCumPropExp(array, maxval(array), sequence)")
70 call disp%show(
"call setCumPropExp(array, maxval(array), selection)")
75 call disp%show(
"array = array(size(array):1:-1)")
76 array
= array(
size(array):
1:
-1)
79 call disp%show(
"call setCumPropExp(array, maxval(array), sequence, backward, nothing)")
80 call setCumPropExp(array,
maxval(array), sequence, backward, nothing)
84 call disp%show(
"call setCumPropExp(array, maxval(array), sequence, backward, reverse)")
85 call setCumPropExp(array,
maxval(array), sequence, backward, reverse)
Allocate or resize (shrink or expand) an input allocatable scalar string or array of rank 1....
Return a uniform random scalar or contiguous array of arbitrary rank of randomly uniformly distribute...
This is a generic method of the derived type display_type with pass attribute.
This is a generic method of the derived type display_type with pass attribute.
This module contains procedures and generic interfaces for resizing allocatable arrays of various typ...
This module contains classes and procedures for computing various statistical quantities related to t...
This module contains classes and procedures for input/output (IO) or generic display operations on st...
type(display_type) disp
This is a scalar module variable an object of type display_type for general display.
This module defines the relevant Fortran kind type-parameters frequently used in the ParaMonte librar...
integer, parameter LK
The default logical kind in the ParaMonte library: kind(.true.) in Fortran, kind(....
integer, parameter IK
The default integer kind in the ParaMonte library: int32 in Fortran, c_int32_t in C-Fortran Interoper...
integer, parameter SK
The default character kind in the ParaMonte library: kind("a") in Fortran, c_char in C-Fortran Intero...
integer, parameter RKH
The scalar integer constant of intrinsic default kind, representing the highest-precision real kind t...
Generate and return an object of type display_type.
Example Unix compile command via Intel ifort compiler ⛓
3ifort -fpp -standard-semantics -O3 -Wl,-rpath,../../../lib -I../../../inc main.F90 ../../../lib/libparamonte* -o main.exe
Example Windows Batch compile command via Intel ifort compiler ⛓
2set PATH=..\..\..\lib;%PATH%
3ifort /fpp /standard-semantics /O3 /I:..\..\..\include main.F90 ..\..\..\lib\libparamonte*.lib /exe:main.exe
Example Unix / MinGW compile command via GNU gfortran compiler ⛓
3gfortran -cpp -ffree-line-length-none -O3 -Wl,-rpath,../../../lib -I../../../inc main.F90 ../../../lib/libparamonte* -o main.exe
Example output ⛓
2array
= log([
1.,
2.,
3.,
4.])
4+0.00000000,
+0.693147182,
+1.09861231,
+1.38629436
8+0.100000001,
+0.300000012,
+0.600000024,
+1.00000000
11+0.100000001,
+0.300000012,
+0.600000024,
+1.00000000
13array
= array(
size(array):
1:
-1)
15+1.38629436,
+1.09861231,
+0.693147182,
+0.00000000
16call setCumPropExp(cumPropExp, array,
maxval(array), sequence, backward, nothing)
18+0.100000001,
+0.300000012,
+0.600000024,
+1.00000000
20call setCumPropExp(cumPropExp, array,
maxval(array), sequence, backward, reverse)
22+1.00000000,
+0.600000024,
+0.300000012,
+0.100000001
30array
= log([
1.,
2.,
3.,
4.])
32+0.00000000,
+0.693147182,
+1.09861231,
+1.38629436
35+0.100000001,
+0.300000012,
+0.600000024,
+1.00000000
38+0.157984704,
+0.350947648,
+0.611420393,
+1.00000000
40array
= array(
size(array):
1:
-1)
42+1.00000000,
+0.611420393,
+0.350947648,
+0.157984704
43call setCumPropExp(array,
maxval(array), sequence, backward, nothing)
45+0.163730785,
+0.362309635,
+0.619974375,
+1.00000000
47call setCumPropExp(array,
maxval(array), sequence, backward, reverse)
49+1.00000000,
+0.836214423,
+0.636450350,
+0.377974689
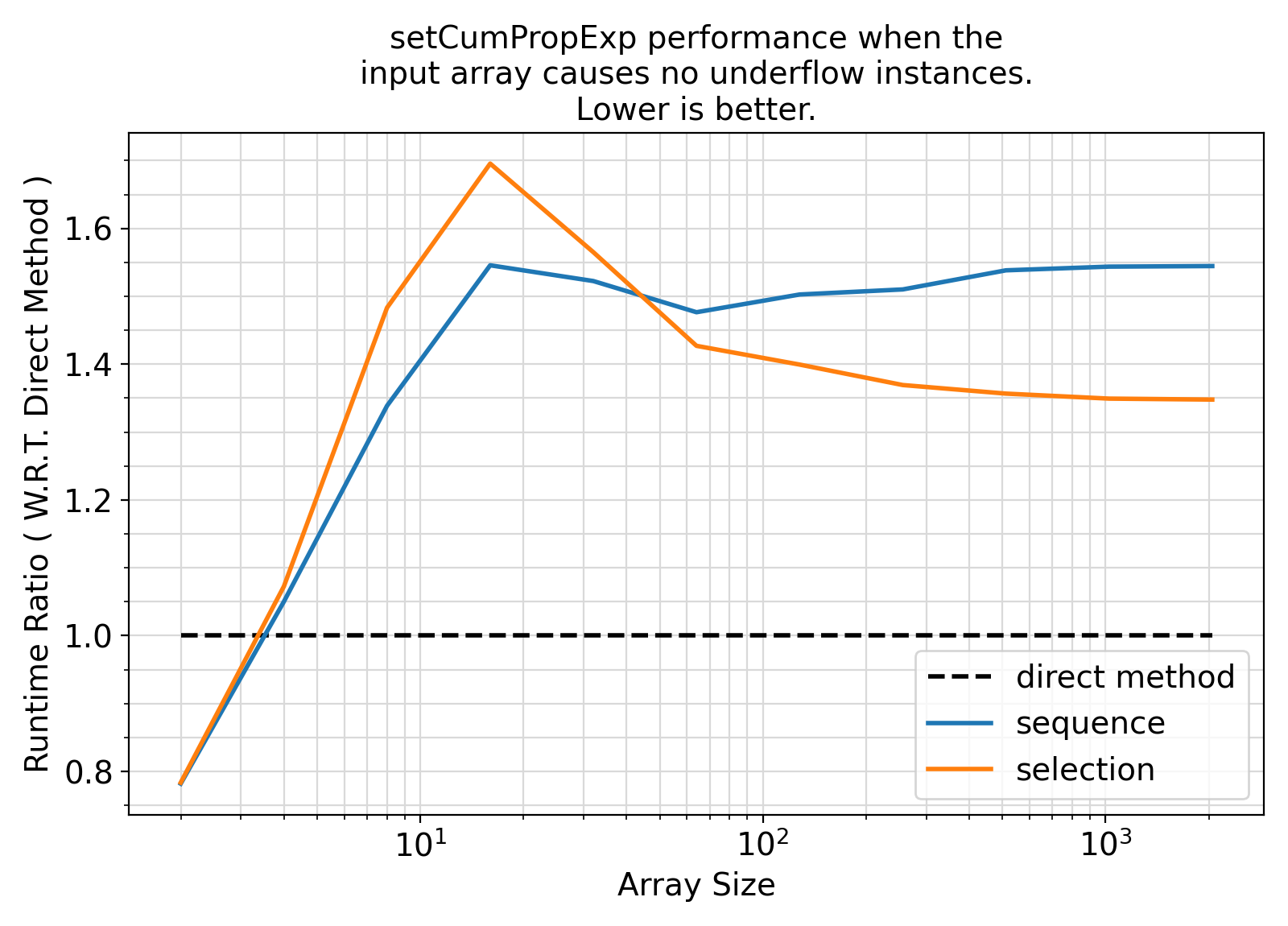
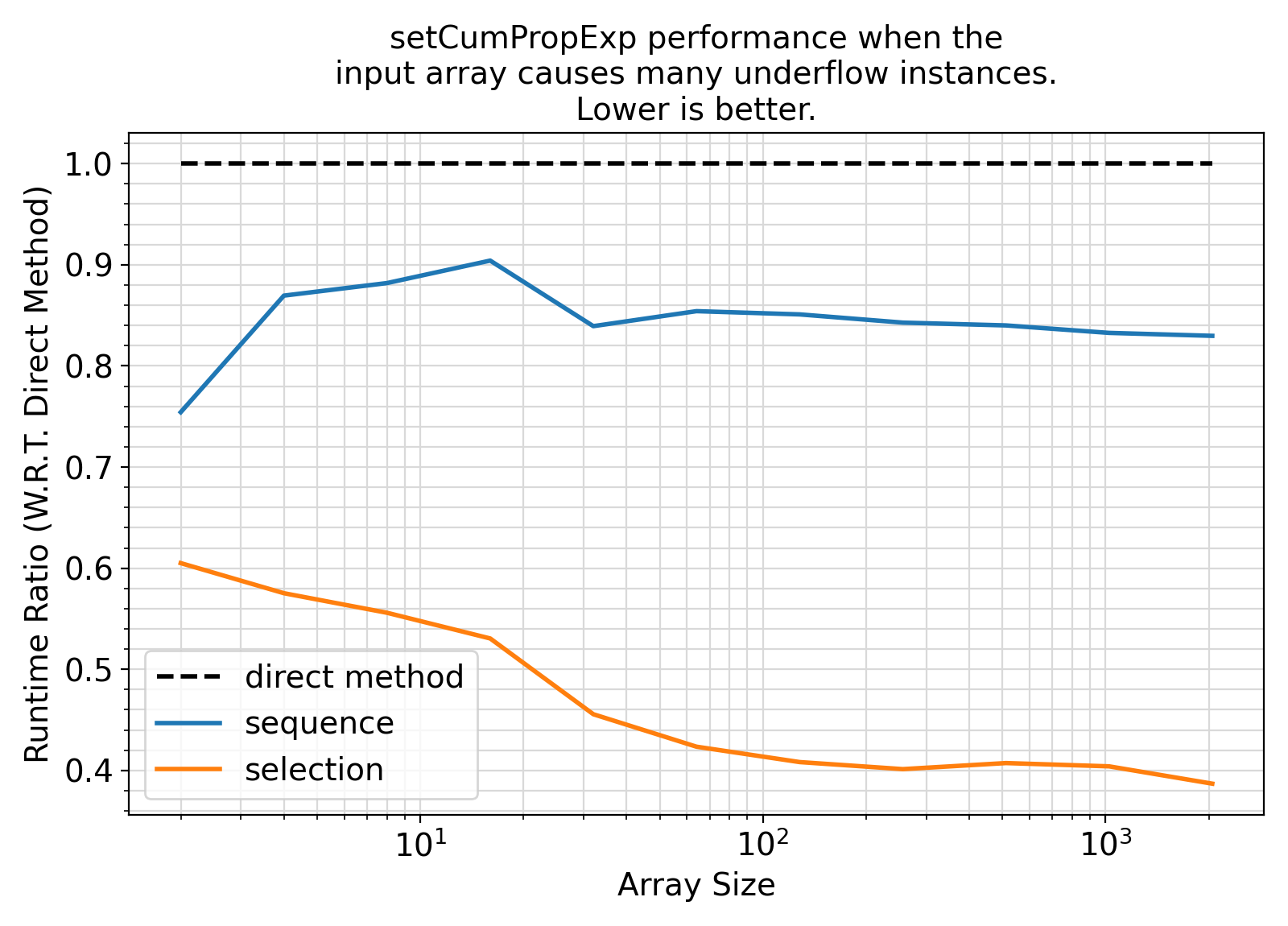
- Benchmarks:
Benchmark :: The effects of control on runtime efficiency ⛓
- The following program compares the runtime performance of setCumPropExp algorithm with and without checking for underflows.
4 use iso_fortran_env,
only:
error_unit
12 integer(IK) :: fileUnitN
13 integer(IK) :: fileUnitU
14 integer(IK) ,
parameter :: NARR
= 11_IK
15 integer(IK) ,
parameter :: NBENCH
= 3_IK
16 integer(IK) :: arraySize(NARR)
17 real(RK) :: dummySum
= 0._RK
19 real(RK) ,
allocatable :: array(:)
20 real(RK) ,
allocatable :: cumPropExp(:)
21 type(bench_type) :: bench(
2,NBENCH)
22 logical(LK) :: underflowEnabled
24 bench(
1:
2,
1)
= bench_type(name
= SK_
"setCumPropExpSequence", exec
= setCumPropExpSequence, overhead
= setOverhead)
25 bench(
1:
2,
2)
= bench_type(name
= SK_
"setCumPropExpSelection", exec
= setCumPropExpSelection, overhead
= setOverhead)
26 bench(
1:
2,
3)
= bench_type(name
= SK_
"setCumPropExpDirect", exec
= setCumPropExpDirect, overhead
= setOverhead)
28 arraySize
= [(
2_IK**iarr, iarr
= 1_IK, NARR )]
30 write(
*,
"(*(g0,:,' '))")
31 write(
*,
"(*(g0,:,' '))")
"setCumPropExp(..., sequence) vs. setCumPropExp(..., selection) vs. direct method."
32 write(
*,
"(*(g0,:,' '))")
34 open(newunit
= fileUnitN, file
= "main.normal.out", status
= "replace")
35 open(newunit
= fileUnitU, file
= "main.underflow.out", status
= "replace")
37 write(fileUnitN,
"(*(g0,:,','))")
"arraySize", (bench(
1,i)
%name, i
= 1, NBENCH)
38 write(fileUnitU,
"(*(g0,:,','))")
"arraySize", (bench(
2,i)
%name, i
= 1, NBENCH)
40 loopOverArraySize:
do iarr
= 1, NARR
42 allocate(array(arraySize(iarr)))
43 allocate(cumPropExp(arraySize(iarr)),
source = 0._RK)
44 write(
*,
"(*(g0,:,' '))")
"Benchmarking with array size", arraySize(iarr)
46 underflowEnabled
= .false._LK
49 bench(
1,i)
%timing
= bench(
1,i)
%getTiming(minsec
= 0.07_RK)
51 write(fileUnitN,
"(*(g0,:,','))") arraySize(iarr), (bench(
1,i)
%timing
%mean, i
= 1, NBENCH)
53 underflowEnabled
= .true._LK
55 bench(
2,i)
%timing
= bench(
2,i)
%getTiming(minsec
= 0.07_RK)
57 write(fileUnitU,
"(*(g0,:,','))") arraySize(iarr), (bench(
2,i)
%timing
%mean, i
= 1, NBENCH)
59 deallocate(array, cumPropExp)
61 end do loopOverArraySize
62 write(
*,
"(*(g0,:,' '))") dummySum
63 write(
*,
"(*(g0,:,' '))")
74 subroutine setOverhead()
80 call random_number(array)
81 if (underflowEnabled) array
= array
* (
maxexponent(
0._RK)
- minexponent(
0._RK))
+ minexponent(
0._RK)
82 maxArray
= maxval(array)
86 dummySum
= dummySum
+ cumPropExp(
1)
+ array(
1)
89 subroutine setCumPropExpSequence()
96 subroutine setCumPropExpSelection()
103 subroutine setCumPropExpDirect()
106 call setCumSum(cumPropExp,
exp(array
- maxArray))
107 cumPropExp
= cumPropExp
/ cumPropExp(
size(cumPropExp))
Generate and return an object of type timing_type containing the benchmark timing information and sta...
Return the cumulative sum of the input array, optionally in the backward direction and optionally,...
This module contains abstract interfaces and types that facilitate benchmarking of different procedur...
integer, parameter RK
The default real kind in the ParaMonte library: real64 in Fortran, c_double in C-Fortran Interoperati...
This module contains the procedures and interfaces for computing the cumulative sum of an array.
This is the class for creating benchmark and performance-profiling objects.
Example Unix compile command via Intel ifort compiler ⛓
3ifort -fpp -standard-semantics -O3 -Wl,-rpath,../../../lib -I../../../inc main.F90 ../../../lib/libparamonte* -o main.exe
Example Windows Batch compile command via Intel ifort compiler ⛓
2set PATH=..\..\..\lib;%PATH%
3ifort /fpp /standard-semantics /O3 /I:..\..\..\include main.F90 ..\..\..\lib\libparamonte*.lib /exe:main.exe
Example Unix / MinGW compile command via GNU gfortran compiler ⛓
3gfortran -cpp -ffree-line-length-none -O3 -Wl,-rpath,../../../lib -I../../../inc main.F90 ../../../lib/libparamonte* -o main.exe
Postprocessing of the benchmark output ⛓
3import matplotlib.pyplot
as plt
9methods = [
"direct method",
"sequence",
"selection"]
15df = pd.read_csv(
"main.normal.out")
17ax = plt.figure(figsize = 1.25 * np.array([6.4,4.6]), dpi = 200)
20plt.plot( df[
"arraySize"].values
21 , np.ones(len(df[
"arraySize"].values))
26plt.plot( df[
"arraySize"].values
27 , df[
"setCumPropExpSequence"].values / df[
"setCumPropExpDirect"].values
30plt.plot( df[
"arraySize"].values
31 , df[
"setCumPropExpSelection"].values / df[
"setCumPropExpDirect"].values
35plt.xticks(fontsize = fontsize)
36plt.yticks(fontsize = fontsize)
37ax.set_xlabel(
"Array Size", fontsize = fontsize)
38ax.set_ylabel(
"Runtime Ratio ( W.R.T. Direct Method )", fontsize = fontsize)
39ax.set_title(
"setCumPropExp performance when the\ninput array causes no underflow instances.\nLower is better.", fontsize = fontsize)
43plt.grid(visible =
True, which =
"both", axis =
"both", color =
"0.85", linestyle =
"-")
44ax.tick_params(axis =
"y", which =
"minor")
45ax.tick_params(axis =
"x", which =
"minor")
53plt.savefig(
"benchmark.setCumPropExp.normal.png")
59df = pd.read_csv(
"main.underflow.out")
61ax = plt.figure(figsize = 1.25 * np.array([6.4,4.6]), dpi = 200)
64plt.plot( df[
"arraySize"].values
65 , np.ones(len(df[
"arraySize"].values))
70plt.plot( df[
"arraySize"].values
71 , df[
"setCumPropExpSequence"].values / df[
"setCumPropExpDirect"].values
74plt.plot( df[
"arraySize"].values
75 , df[
"setCumPropExpSelection"].values / df[
"setCumPropExpDirect"].values
79plt.xticks(fontsize = fontsize)
80plt.yticks(fontsize = fontsize)
81ax.set_xlabel(
"Array Size", fontsize = fontsize)
82ax.set_ylabel(
"Runtime Ratio (W.R.T. Direct Method)", fontsize = fontsize)
83ax.set_title(
"setCumPropExp performance when the\ninput array causes many underflow instances.\nLower is better.", fontsize = fontsize)
87plt.grid(visible =
True, which =
"both", axis =
"both", color =
"0.85", linestyle =
"-")
88ax.tick_params(axis =
"y", which =
"minor")
89ax.tick_params(axis =
"x", which =
"minor")
97plt.savefig(
"benchmark.setCumPropExp.underflow.png")
Visualization of the benchmark output ⛓
Benchmark moral ⛓
- If the input array has many (half the size of array or more) elements whose division by the
maxval(array) causes underflow, then setting control = selection when calling setCumPropExp will likely result in a faster runtime.
Conversely, if the divisions are not expected to cause any or too many underflows, then set control = selection to improve cache coherence and runtime performance (at the expense of occasional expensive but redundant exponentiations).
- If the input array size is less than 10-20 elements and setCumPropExp is to be called billions of times, then it would make sense to manually inline the procedure implementation in your code as procedure call and processing of optional arguments will have a non-negligible performance overhead.
- Test:
- test_pm_mathCumPropExp
- Todo:
- Low Priority: This generic interface can be expanded to include input arrays with
Weights.
Final Remarks ⛓
If you believe this algorithm or its documentation can be improved, we appreciate your contribution and help to edit this page's documentation and source file on GitHub.
For details on the naming abbreviations, see this page.
For details on the naming conventions, see this page.
This software is distributed under the MIT license with additional terms outlined below.
-
If you use any parts or concepts from this library to any extent, please acknowledge the usage by citing the relevant publications of the ParaMonte library.
-
If you regenerate any parts/ideas from this library in a programming environment other than those currently supported by this ParaMonte library (i.e., other than C, C++, Fortran, MATLAB, Python, R), please also ask the end users to cite this original ParaMonte library.
This software is available to the public under a highly permissive license.
Help us justify its continued development and maintenance by acknowledging its benefit to society, distributing it, and contributing to it.
- Copyright
- Computational Data Science Lab
- Author:
- Amir Shahmoradi, April 25, 2015, 2:21 PM, National Institute for Fusion Studies, The University of Texas Austin
Definition at line 569 of file pm_mathCumPropExp.F90.