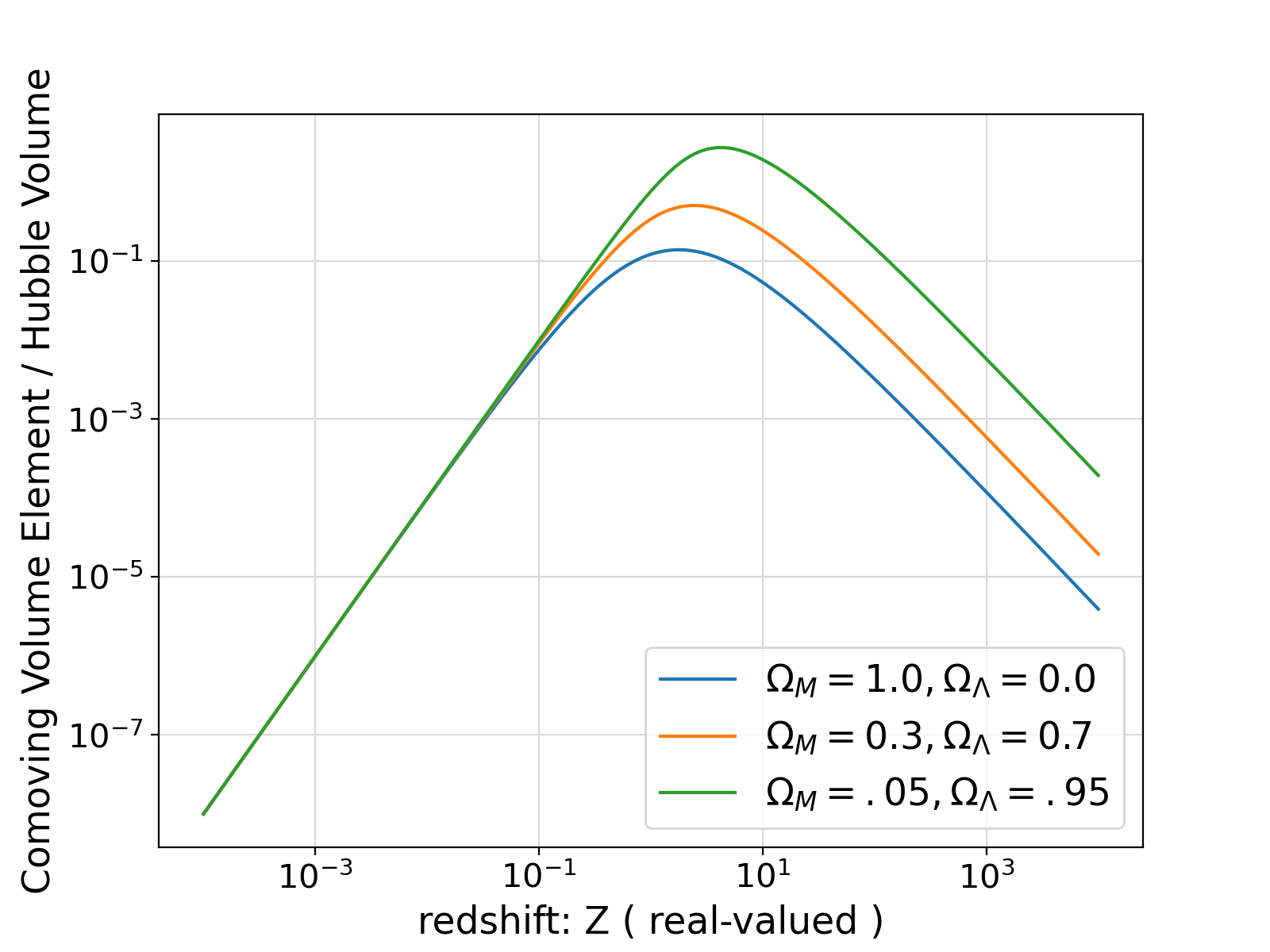
Generate and return the cosmological Comoving Volume Differential (Element) per unit solid angle of the sky (i.e., 1 Steradian normalized to Hubble Volume, given the user-specified cosmological parameters.
Assuming (\Omega_M, \Omega_\Lambda, \Omega_R, \Omega_K) represent the normalized densities of Dark Matter, Dark Energy, Radiation Energy, and Curvature in a Universe with negligible neutrino mass such that \Omega_M + \Omega_\Lambda + \Omega_R + \Omega_K = 1, the Comoving Volume Element dV_C at a given cosmological redshift z is defined as (e.g., Peebles, 1993),
\begin{eqnarray}
\large
dV_C(z; \Omega_M, \Omega_\Lambda, \Omega_R, \Omega_K)
&=& D_H \frac{\big[D_M(z; \Omega_M, \Omega_\Lambda, \Omega_R, \Omega_K)\big]^2}{E(z; \Omega_M, \Omega_\Lambda, \Omega_R, \Omega_K)} ~ dz ~ d\Omega ~, \\
&=& D_H \frac{\big[D_A(z; \Omega_M, \Omega_\Lambda, \Omega_R, \Omega_K)\big]^2}{E(z; \Omega_M, \Omega_\Lambda, \Omega_R, \Omega_K)} (1+z)^2 ~ dz ~ d\Omega ~, \\
&=& D_H \frac{\big[D_L(z; \Omega_M, \Omega_\Lambda, \Omega_R, \Omega_K)\big]^2}{E(z; \Omega_M, \Omega_\Lambda, \Omega_R, \Omega_K)} \frac{1}{(1+z)^2} ~ dz ~ d\Omega ~,
\end{eqnarray}
where
- dV_C(z; \cdots) is the cosmological Comoving Volume Element at redshift z,,
- D_M(z; \cdots) is the cosmological Transverse Comoving Distance as a subroutine of redshift,
- D_A(z; \cdots) is the cosmological Angular Diameter Distance as a subroutine of redshift,
- D_L(z; \cdots) is the cosmological Luminosity Distance as a subroutine of redshift,
- E(z; \cdots) is the dimensionless Hubble Parameter,
- D_H = \frac{C}{H_0} is the Hubble Distance,
- H_0 is the Hubble Constant.
- C is the speed of light,
- z is the redshift,
The value returned by the procedures under this generic interface is \frac{dV_C}{V_H}, that is, normalized to the Hubble Volume.
To obtain the full-sky (normalized) Comoving Volume Element, multiply the output of the procedures under this generic interface by 4\pi, that is, 4 * acos(-1.).
- Parameters
-
| [out] | volComDiffNormed | : The output scalar or array of the same rank as other array-like arguments, of the same type and kind as the input argument zplus1 containing the cosmological Comoving Volume Element per Steradian at the desired redshift normalized to the Hubble Distance. |
| [in] | disComTransNormedSq | : The input scalar or array of the same rank as other array-like arguments, of type real of kind any supported by the processor (e.g., RK, RK32, RK64, or RK128) representing the the square of the Dimensionless (Normalized) Transverse Comoving Distance at the desired redshift for which the Comoving Volume Element must be computed.
This argument can be readily obtained by taking the square of the output of getDisComTransNormed, or if the cosmology is the Concordance model, one can use the approximation provided by getDisComTransNormedWU10.
See the examples below for usage.
|
| [in] | hubbleParamNormed | : The input scalar or array of the same rank as other array-like arguments, of the same type and kind as disComTransNormedSq representing the Dimensionless Hubble Parameter at the desired redshift for which the Comoving Volume Element must be computed.
This argument can be readily obtained by taking the square-root of the output of getHubbleParamNormedSq.
See the examples below for usage.
|
Possible calling interfaces ⛓
Generate and return the cosmological Comoving Volume Differential (Element) per unit solid angle of t...
This module contains procedures and generic interfaces and constants for cosmological calculations.
- Warning
- The input arguments must be computed for the same redshift and cosmological parameters.
The equivalence and consistencies of the input arguments are not verified within the algorithm because such validations require extra information that is not provided as input.
- Developer Remark:
- There is no performance benefit in passing the inverse of
hubbleParamNormed instead of the what is passed in the current interface.
Do not attempt to change the interface.
- See also
- getVolComNormed
getHubbleParamNormedSq
getDisComTransNormed
getDisLumNormed
getDisAngNormed
getDisComNormed
LOG_HUBBLE_CONST
HUBBLE_DISTANCE_MPC
HUBBLE_CONST
OMEGA_M
OMEGA_L
OMEGA_R
OMEGA_K
Example usage ⛓
11 real :: VolComDiffNormed(
3)
12 type(display_type) :: disp
17 call disp%show(
"!%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%")
18 call disp%show(
"!Compute the Comoving Volume Element in units of Hubble Volume.")
19 call disp%show(
"!%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%")
23 call disp%show(
"call setVolComDiffNormed(VolComDiffNormed(1), getDisComTransNormed(zplus1 = 1., reltol = sqrt(epsilon(0.)))**2, sqrt(getHubbleParamNormedSq(zplus1 = 1.)))")
25 call disp%show(
"VolComDiffNormed(1)")
26 call disp%show( VolComDiffNormed(
1) )
30 call disp%show(
"call setVolComDiffNormed(VolComDiffNormed(1), getDisComTransNormed(zplus1 = 1.1, reltol = sqrt(epsilon(0.)))**2, sqrt(getHubbleParamNormedSq(zplus1 = 1.1)))")
32 call disp%show(
"VolComDiffNormed(1)")
33 call disp%show( VolComDiffNormed(
1) )
37 call disp%show(
"call setVolComDiffNormed(VolComDiffNormed(1:2), getDisComTransNormed(zplus1 = [ 2., 3.], omegaM = 0.4, omegaL = 0.6, reltol = 0.0001)**2, sqrt(getHubbleParamNormedSq(zplus1 = [ 2., 3.], omegaM = 0.4, omegaL = 0.6)))")
39 call disp%show(
"VolComDiffNormed(1:2)")
40 call disp%show( VolComDiffNormed(
1:
2) )
44 call disp%show(
"call setVolComDiffNormed(VolComDiffNormed(1:2), getDisComTransNormed(zplus1 = [ 2., 3.], omegaM = 0.2, omegaL = 0.6, omegaR = 0.2, reltol = 0.0001)**2, sqrt(getHubbleParamNormedSq(zplus1 = [ 2., 3.], omegaM = 0.2, omegaL = 0.6, omegaR = 0.2)))")
45 call setVolComDiffNormed(VolComDiffNormed(
1:
2),
getDisComTransNormed(zplus1
= [
2.,
3.], omegaM
= 0.2, omegaL
= 0.6, omegaR
= 0.2, reltol
= 0.0001)
**2,
sqrt(
getHubbleParamNormedSq(zplus1
= [
2.,
3.], omegaM
= 0.2, omegaL
= 0.6, omegaR
= 0.2)))
46 call disp%show(
"VolComDiffNormed(1:2)")
47 call disp%show( VolComDiffNormed(
1:
2) )
51 call disp%show(
"call setVolComDiffNormed(VolComDiffNormed(1:2), getDisComTransNormed(zplus1 = [ 2., 3.], omegaM = 0.2, omegaL = 0.6, omegaR = 0.4, omegaK = -0.2, sqrtAbsOmegaK = sqrt(0.2), reltol = 0.0001)**2, sqrt(getHubbleParamNormedSq(zplus1 = [ 2., 3.], omegaM = 0.2, omegaL = 0.6, omegaR = 0.4, omegaK = -0.2)))")
52 call setVolComDiffNormed(VolComDiffNormed(
1:
2),
getDisComTransNormed(zplus1
= [
2.,
3.], omegaM
= 0.2, omegaL
= 0.6, omegaR
= 0.4, omegaK
= -0.2, sqrtAbsOmegaK
= sqrt(
0.2), reltol
= 0.0001)
**2,
sqrt(
getHubbleParamNormedSq(zplus1
= [
2.,
3.], omegaM
= 0.2, omegaL
= 0.6, omegaR
= 0.4, omegaK
= -0.2)))
53 call disp%show(
"VolComDiffNormed(1:2)")
54 call disp%show( VolComDiffNormed(
1:
2) )
65 real,
allocatable :: zplus1(:), OmegaM(:), OmegaL(:), VolComDiffNormed(:)
66 integer :: fileUnit, i
68 OmegaM
= [
1.,
0.3, .
05]
70 allocate(VolComDiffNormed,
mold = OmegaM)
71 zplus1
= 1. + getLogSpace(
log(
0.0001),
log(
10000.),
500_IK)
73 open(newunit
= fileUnit, file
= "setVolComDiffNormed.RK.txt")
74 write(fileUnit,
"(*(g0,:,','))")
"z", (
"DisLum_"//getStr(OmegaM(i),
"(g0.1)")
//"_"//getStr(OmegaL(i),
"(g0.1)"), i
= 1,
size(OmegaM))
75 do i
= 1,
size(zplus1)
77 write(fileUnit,
"(*(g0,:,','))") zplus1(i)
- 1., VolComDiffNormed
Generate count evenly spaced points over the interval [x1, x2] if x1 < x2, or [x2,...
Generate count evenly-logarithmically-spaced points over the interval [base**logx1,...
Generate and return the cosmological Transverse Comoving Distance normalized to Hubble Distance,...
Generate and return the square of the dimensionless Hubble Parameter for the default or the specifie...
This is a generic method of the derived type display_type with pass attribute.
This is a generic method of the derived type display_type with pass attribute.
Generate and return the conversion of the input value to an output Fortran string,...
This module contains procedures and generic interfaces for generating arrays with linear or logarithm...
This module contains classes and procedures for input/output (IO) or generic display operations on st...
type(display_type) disp
This is a scalar module variable an object of type display_type for general display.
This module defines the relevant Fortran kind type-parameters frequently used in the ParaMonte librar...
integer, parameter IK
The default integer kind in the ParaMonte library: int32 in Fortran, c_int32_t in C-Fortran Interoper...
integer, parameter SK
The default character kind in the ParaMonte library: kind("a") in Fortran, c_char in C-Fortran Intero...
This module contains the generic procedures for converting values of different types and kinds to For...
Generate and return an object of type display_type.
Example Unix compile command via Intel ifort compiler ⛓
3ifort -fpp -standard-semantics -O3 -Wl,-rpath,../../../lib -I../../../inc main.F90 ../../../lib/libparamonte* -o main.exe
Example Windows Batch compile command via Intel ifort compiler ⛓
2set PATH=..\..\..\lib;%PATH%
3ifort /fpp /standard-semantics /O3 /I:..\..\..\include main.F90 ..\..\..\lib\libparamonte*.lib /exe:main.exe
Example Unix / MinGW compile command via GNU gfortran compiler ⛓
3gfortran -cpp -ffree-line-length-none -O3 -Wl,-rpath,../../../lib -I../../../inc main.F90 ../../../lib/libparamonte* -o main.exe
Example output ⛓
19+0.273632020,
+0.371431828
22call setVolComDiffNormed(VolComDiffNormed(
1:
2),
getDisComTransNormed(zplus1
= [
2.,
3.], omegaM
= 0.2, omegaL
= 0.6, omegaR
= 0.2, reltol
= 0.0001)
**2,
sqrt(
getHubbleParamNormedSq(zplus1
= [
2.,
3.], omegaM
= 0.2, omegaL
= 0.6, omegaR
= 0.2)))
24+0.199308142,
+0.205419630
27call setVolComDiffNormed(VolComDiffNormed(
1:
2),
getDisComTransNormed(zplus1
= [
2.,
3.], omegaM
= 0.2, omegaL
= 0.6, omegaR
= 0.4, omegaK
= -0.2, sqrtAbsOmegaK
= sqrt(
0.2), reltol
= 0.0001)
**2,
sqrt(
getHubbleParamNormedSq(zplus1
= [
2.,
3.], omegaM
= 0.2, omegaL
= 0.6, omegaR
= 0.4, omegaK
= -0.2)))
29+0.135484368,
+0.118126549
Postprocessing of the example output ⛓
3import matplotlib.pyplot
as plt
15xlab = {
"CK" :
"redshift: Z ( real/imaginary components )"
16 ,
"IK" :
"redshift: Z ( integer-valued )"
17 ,
"RK" :
"redshift: Z ( real-valued )"
19legends = [
"$\Omega_M = 1.0, \Omega_\Lambda = 0.0$"
20 ,
"$\Omega_M = 0.3, \Omega_\Lambda = 0.7$"
21 ,
"$\Omega_M = .05, \Omega_\Lambda = .95$"
24for kind
in [
"IK",
"CK",
"RK"]:
26 pattern =
"*." + kind +
".txt"
27 fileList = glob.glob(pattern)
28 if len(fileList) == 1:
30 df = pd.read_csv(fileList[0], delimiter =
",")
32 fig = plt.figure(figsize = 1.25 * np.array([6.4, 4.8]), dpi = 200)
36 plt.plot( df.values[:, 0]
37 , df.values[:,1:len(legends)+1]
41 plt.plot( df.values[:, 1]
42 , df.values[:,1:len(legends)+1]
47 plt.plot( df.values[:, 0]
48 , df.values[:,1:len(legends)+1]
56 plt.xticks(fontsize = fontsize - 2)
57 plt.yticks(fontsize = fontsize - 2)
58 ax.set_xlabel(xlab[kind], fontsize = 17)
59 ax.set_ylabel(
"Comoving Volume Element / Hubble Volume", fontsize = 17)
60 plt.grid(visible =
True, which =
"both", axis =
"both", color =
"0.85", linestyle =
"-")
61 ax.tick_params(axis =
"y", which =
"minor")
62 ax.tick_params(axis =
"x", which =
"minor")
66 plt.savefig(fileList[0].replace(
".txt",
".png"))
68 elif len(fileList) > 1:
70 sys.exit(
"Ambiguous file list exists.")
Visualization of the example output ⛓
- Test:
- test_pm_cosmology
Final Remarks ⛓
If you believe this algorithm or its documentation can be improved, we appreciate your contribution and help to edit this page's documentation and source file on GitHub.
For details on the naming abbreviations, see this page.
For details on the naming conventions, see this page.
This software is distributed under the MIT license with additional terms outlined below.
-
If you use any parts or concepts from this library to any extent, please acknowledge the usage by citing the relevant publications of the ParaMonte library.
-
If you regenerate any parts/ideas from this library in a programming environment other than those currently supported by this ParaMonte library (i.e., other than C, C++, Fortran, MATLAB, Python, R), please also ask the end users to cite this original ParaMonte library.
This software is available to the public under a highly permissive license.
Help us justify its continued development and maintenance by acknowledging its benefit to society, distributing it, and contributing to it.
- Copyright
- Computational Data Science Lab
- Author:
- Amir Shahmoradi, September 1, 2012, 12:00 AM, National Institute for Fusion Studies, The University of Texas Austin
Definition at line 3723 of file pm_cosmology.F90.