|
ParaMonte MATLAB 3.0.0
Parallel Monte Carlo and Machine Learning Library
See the latest version documentation. |
|
ParaMonte MATLAB 3.0.0
Parallel Monte Carlo and Machine Learning Library
See the latest version documentation. |
This is the SubplotHeatmap class for generating instances of 2-dimensional Heatmap Subplot visualizations based on the relevant MATLAB intrinsic functions.
More...
Public Member Functions | |
| function | SubplotHeatmap (in dfref, in varargin) |
| Construct and return an object of class pm.vis.SubplotHeatmap. More... | |
| function | setColorLim (in self, in lb, in ub) |
Reset the heatmap colormap limits to the user-specified limits lb and ub.If either is empty or missing, keep the existing limit for the corresponding empty limit. If both are empty or missing, symmetrize the existing limits. The specified input values will be used to set the ColorLimits component of the Heatmap object as ColorLimits = [lb, ub].If both input values are missing, the current colormap range of the Heatmap subplots will be symmetrized. More... | |
This is the SubplotHeatmap class for generating instances of 2-dimensional Heatmap Subplot visualizations based on the relevant MATLAB intrinsic functions.
Final Remarks ⛓
If you believe this algorithm or its documentation can be improved, we appreciate your contribution and help to edit this page's documentation and source file on GitHub.
For details on the naming abbreviations, see this page.
For details on the naming conventions, see this page.
This software is distributed under the MIT license with additional terms outlined below.
This software is available to the public under a highly permissive license.
Help us justify its continued development and maintenance by acknowledging its benefit to society, distributing it, and contributing to it.
Definition at line 25 of file SubplotHeatmap.m.
| function SubplotHeatmap::SubplotHeatmap | ( | in | dfref, |
| in | varargin | ||
| ) |
Construct and return an object of class pm.vis.SubplotHeatmap.
This is the constructor of the class pm.vis.SubplotHeatmap.
| [in] | dfref | : See the documentation of the corresponding input argument of the superclass pm.vis.Subplot. |
| [in] | varargin | : Any property, value pair of the parent object.If the property is a struct(), then its value must be given as a cell array, with consecutive elements representing the struct property-name, property-value pairs.Note that all of these property-value pairs can be also directly set via the parent object attributes, before calling the make() method. |
self : The output object of class pm.vis.SubplotHeatmap.
Possible calling interfaces ⛓
Example usage ⛓
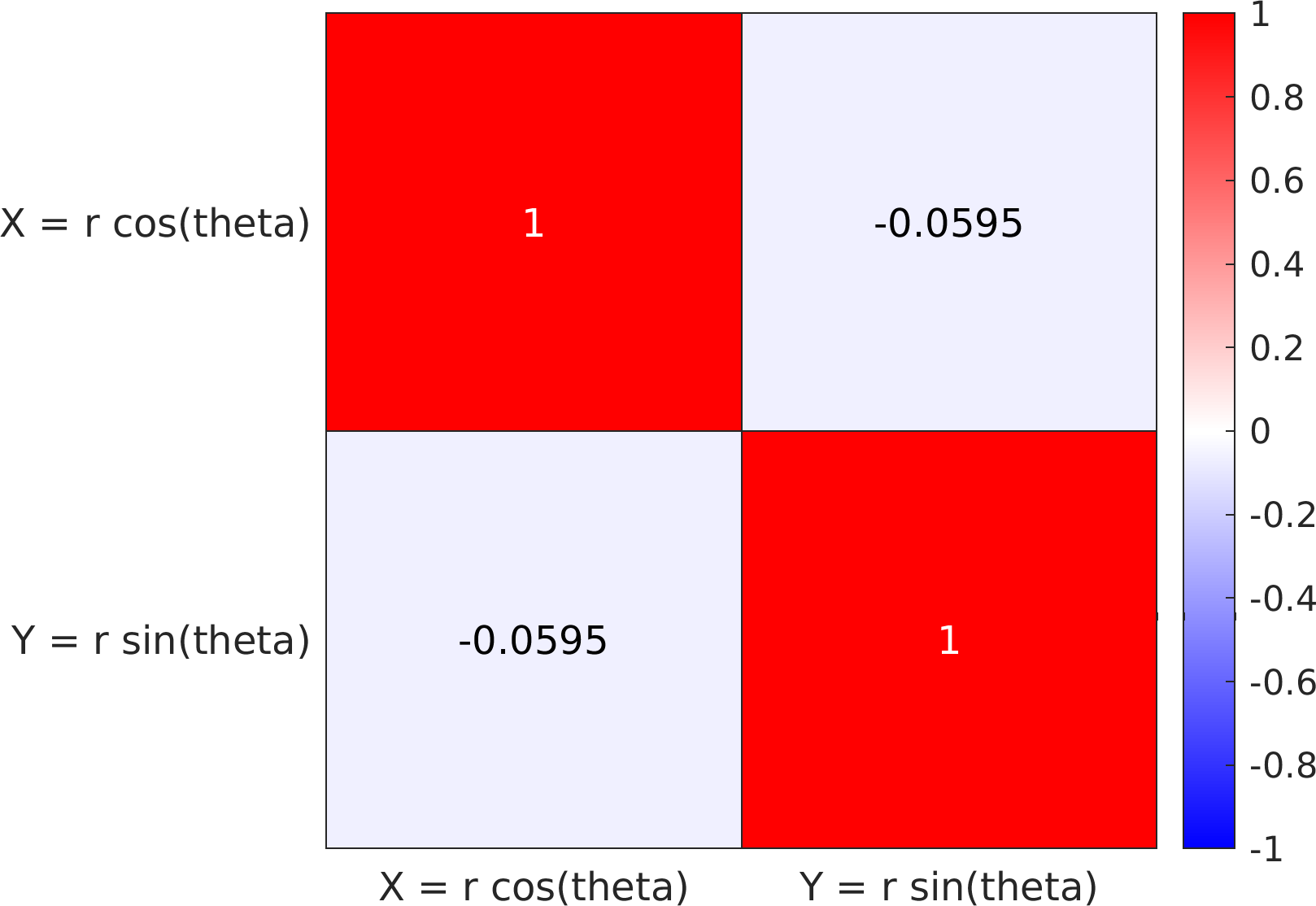
Final Remarks ⛓
If you believe this algorithm or its documentation can be improved, we appreciate your contribution and help to edit this page's documentation and source file on GitHub.
For details on the naming abbreviations, see this page.
For details on the naming conventions, see this page.
This software is distributed under the MIT license with additional terms outlined below.
This software is available to the public under a highly permissive license.
Help us justify its continued development and maintenance by acknowledging its benefit to society, distributing it, and contributing to it.
| function SubplotHeatmap::setColorLim | ( | in | self, |
| in | lb, | ||
| in | ub | ||
| ) |
Reset the heatmap colormap limits to the user-specified limits lb and ub.
If either is empty or missing, keep the existing limit for the corresponding empty limit.
If both are empty or missing, symmetrize the existing limits.
The specified input values will be used to set the ColorLimits component of the Heatmap object as ColorLimits = [lb, ub].
If both input values are missing, the current colormap range of the Heatmap subplots will be symmetrized.
| [in] | self | : The implicitly-passed input argument representing the parent object of the method. |
| [in] | lb | : The input MATLAB object that can be either:
|
| [in] | ub | : The input MATLAB scalar double representing the upper bound of the Heatmap colormap limits. Its value is completely ignored if the input lb argument is a vector of size 2.(optional. If missing, the current value will remain intact.) |
Possible calling interfaces ⛓
Example usage ⛓
Example usage ⛓

Final Remarks ⛓
If you believe this algorithm or its documentation can be improved, we appreciate your contribution and help to edit this page's documentation and source file on GitHub.
For details on the naming abbreviations, see this page.
For details on the naming conventions, see this page.
This software is distributed under the MIT license with additional terms outlined below.
This software is available to the public under a highly permissive license.
Help us justify its continued development and maintenance by acknowledging its benefit to society, distributing it, and contributing to it.