|
ParaMonte MATLAB 3.0.0
Parallel Monte Carlo and Machine Learning Library
See the latest version documentation. |
|
ParaMonte MATLAB 3.0.0
Parallel Monte Carlo and Machine Learning Library
See the latest version documentation. |
This is the base class for generating objects with methods and storage components for computing, storing, and visualizing the correlation matrix of an input data.
More...
Public Member Functions | |
| function | Cor (in dfref, in method) |
| Return an object of class pm.stats.Cor. More... | |
| function | get (in self, in dfref, in method) |
| Return the correlation matrix of the input data. More... | |
| function | setvis (in self, in val) |
| Set up the visualization tools of the correlation matrix. More... | |
This is the base class for generating objects with methods and storage components for computing, storing, and visualizing the correlation matrix of an input data.
This is convenience class for easy correlation computation and its storage and visualization all in one place.
The primary advantage of this class over the MATLAB intrinsic functions is in the ability of this class to compute the result for input dataframe table and return the results always in MATLAB table format.
Final Remarks ⛓
If you believe this algorithm or its documentation can be improved, we appreciate your contribution and help to edit this page's documentation and source file on GitHub.
For details on the naming abbreviations, see this page.
For details on the naming conventions, see this page.
This software is distributed under the MIT license with additional terms outlined below.
This software is available to the public under a highly permissive license.
Help us justify its continued development and maintenance by acknowledging its benefit to society, distributing it, and contributing to it.
| function Cor::Cor | ( | in | dfref, |
| in | method | ||
| ) |
Return an object of class pm.stats.Cor.
This is the constructor of the pm.stats.Cor class.
| [in] | dfref | : The input MATLAB matrix or table of rank 2 containing the data as ncol columns of nrow observations whose correlation matrix must be computed.Ideally, the user would want to pass a reference to a dataframe (e.g., as a function handle @()df) so that the data remains dynamically up-to-date.(optional. If missing or empty, the correlation matrix will not be computed.) |
| [in] | method | : The input scalar MATLAB string that can be either:
"pearson") |
self : The output object of class pm.stats.Cor.
Possible calling interfaces ⛓
Example usage ⛓
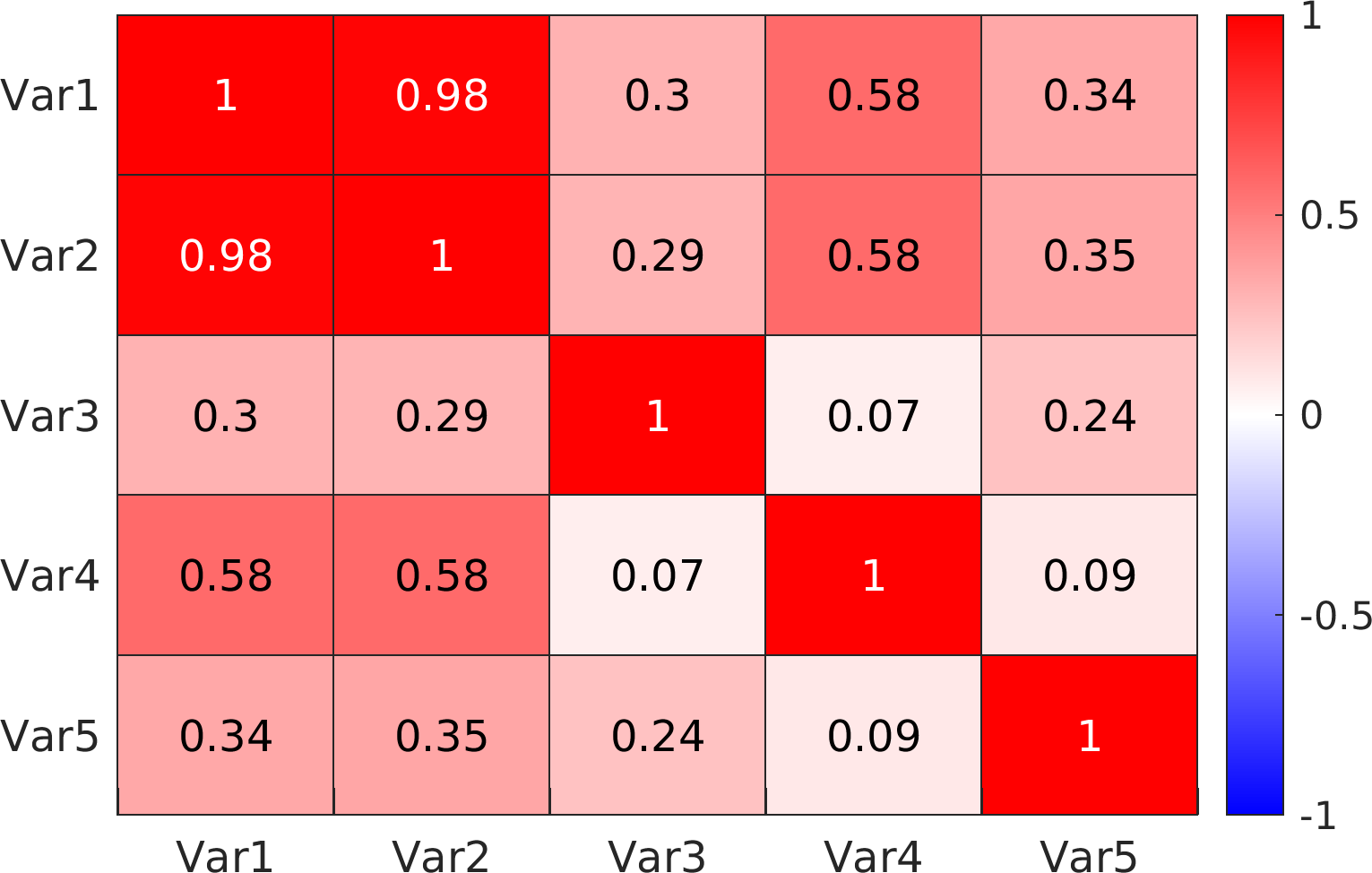
Final Remarks ⛓
If you believe this algorithm or its documentation can be improved, we appreciate your contribution and help to edit this page's documentation and source file on GitHub.
For details on the naming abbreviations, see this page.
For details on the naming conventions, see this page.
This software is distributed under the MIT license with additional terms outlined below.
This software is available to the public under a highly permissive license.
Help us justify its continued development and maintenance by acknowledging its benefit to society, distributing it, and contributing to it.
| function Cor::get | ( | in | self, |
| in | dfref, | ||
| in | method | ||
| ) |
Return the correlation matrix of the input data.
This is a dynamic method of the Cor class.
This method automatically stores any input information in the corresponding components of the parent object.
However, any components of the parent object corresponding to the output of this method must be set explicitly manually.
| [in,out] | self | : The implicitly-passed input argument representing the parent object of the method. |
| [in] | dfref | : The input (reference to a function handle returning a) MATLAB matrix or table of rank 2 containing the ncol columns of nrow data whose correlation matrix must be computed.Ideally, the user would want to pass a reference to a dataframe (e.g., as a function handle @()df) so that the data remains dynamically up-to-date.(optional. If missing, the correlation matrix will not be computed.) |
| [in] | method | : The input scalar MATLAB string that can be either:
"pearson") |
val : The output MATLAB table containing the correlation matrix.
Possible calling interfaces ⛓
Final Remarks ⛓
If you believe this algorithm or its documentation can be improved, we appreciate your contribution and help to edit this page's documentation and source file on GitHub.
For details on the naming abbreviations, see this page.
For details on the naming conventions, see this page.
This software is distributed under the MIT license with additional terms outlined below.
This software is available to the public under a highly permissive license.
Help us justify its continued development and maintenance by acknowledging its benefit to society, distributing it, and contributing to it.
| function Cor::setvis | ( | in | self, |
| in | val | ||
| ) |
Set up the visualization tools of the correlation matrix.
This is a dynamic Hidden method of the pm.stats.Cor class.
This method is inaccessible to the end users of the ParaMonte MATLAB library.
| [in,out] | self | : The implicitly-passed input argument representing the parent object of the method. |
| [in] | val | : The input (reference to a function handle returning a) MATLAB matrix or table of rank 2 containing the computed correlation matrix to be visualized.Ideally, the user would want to pass a reference to a dataframe (e.g., as a function handle @()df) so that the data remains dynamically up-to-date.(optional. If missing, the contents of the corresponding var attribute of the parent object will be used.) |
Possible calling interfaces ⛓
Final Remarks ⛓
If you believe this algorithm or its documentation can be improved, we appreciate your contribution and help to edit this page's documentation and source file on GitHub.
For details on the naming abbreviations, see this page.
For details on the naming conventions, see this page.
This software is distributed under the MIT license with additional terms outlined below.
This software is available to the public under a highly permissive license.
Help us justify its continued development and maintenance by acknowledging its benefit to society, distributing it, and contributing to it.