|
ParaMonte MATLAB 3.0.0
Parallel Monte Carlo and Machine Learning Library
See the latest version documentation. |
|
ParaMonte MATLAB 3.0.0
Parallel Monte Carlo and Machine Learning Library
See the latest version documentation. |
Go to the source code of this file.
Functions | |
| function | getRand (in mean, in cholow, in s1) |
| Return a (set of) multivariate Normal random vector(s). More... | |
| function getRand | ( | in | mean, |
| in | cholow, | ||
| in | s1 | ||
| ) |
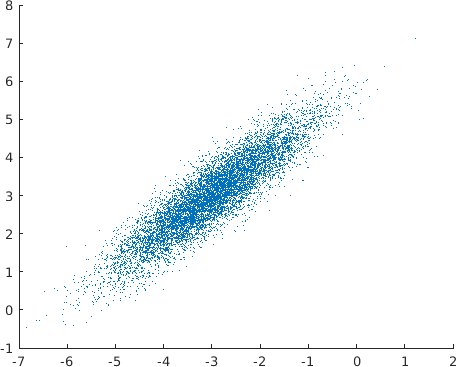
Return a (set of) multivariate Normal random vector(s).
This RNG function can be potentially faster than the intrinsic MATLAB equivalent because it uses the Cholesky factorization of the distribution covariance matrix.
| [in] | mean | : The input vector of MATLAB real, representing the mean of a Multivariate Normal distribution in size(mean) dimensional space.(optional. default = []. It must be present if cholow is missing.) |
| [in] | cholow | : The input square matrix of MATLAB real, representing the lower-triangle of the Cholesky factorization of the covariance matrix of the target Multivariate Normal distribution in numel(mean) dimensional space.This argument can be obtained by passing the covariance matrix covmat of the distribution to the MATLAB intrinsic function chol(covmat, "lower").(optional. default = []. It must be present if mean is missing.) |
| [in] | s1 | : The input scalar MATLAB whole-number, representing the number of random vectors to generate. (optional. default = 1) |
rand : The output vector of MATLAB real of shape (numel(mean), 1) containing a random vector from the specified Multivariate Normal distribution.
Possible calling interfaces ⛓
Example usage ⛓
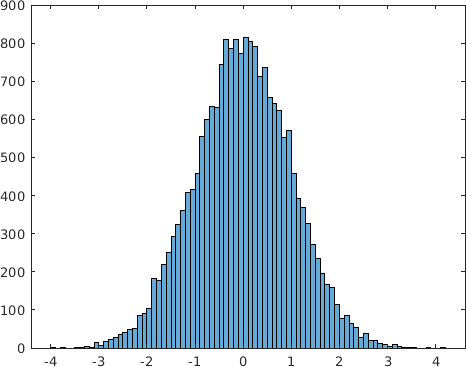
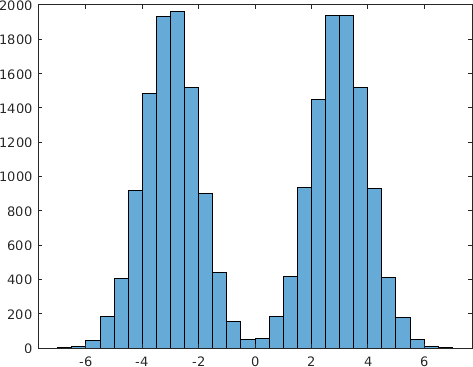
Final Remarks ⛓
If you believe this algorithm or its documentation can be improved, we appreciate your contribution and help to edit this page's documentation and source file on GitHub.
For details on the naming abbreviations, see this page.
For details on the naming conventions, see this page.
This software is distributed under the MIT license with additional terms outlined below.
This software is available to the public under a highly permissive license.
Help us justify its continued development and maintenance by acknowledging its benefit to society, distributing it, and contributing to it.