Return a scalar or array of arbitrary rank of random values from the standard univariate Normal distribution.
More...
Return a scalar or array of arbitrary rank of random values from the standard univariate Normal distribution.
The procedures of this generic interface use the Ziggurat rejection method to generate Normal-distributed random numbers.
- Parameters
-
| [in,out] | rng | : The input/output scalar that can be an object of,
-
type rngf_type, implying the use of intrinsic Fortran uniform RNG for Gamma RNG.
-
type xoshiro256ssw_type, implying the use of xoshiro256** uniform RNG for Normal RNG.
(optional, default = rngf_type, implying the use of the intrinsic Fortran RNG.) |
| [out] | rand | : The output
-
scalar, or
-
array of rank
1, or
-
array of arbitrary rank if the
rng argument is missing or set to rngf_type, or
of,
-
type
real of kind any supported by the processor (e.g., RK, RK32, RK64, or RK128).
On output, it contains standard Normal-distributed random value(s).
|
| [in] | zig | : The input matrix of shape (1:2, 0:*) of the same type and kind as the output argument rand, containing the information about the Ziggurat layers.
This matrix is directly (and must have been) returned by getZigNorm.
(optional. default = ZIG_RKB) |
Possible calling interfaces ⛓
Return a scalar or array of arbitrary rank of random values from the standard univariate Normal distr...
This module contains classes and procedures for computing various statistical quantities related to t...
- Warning
- The condition
precision(rand) <= ZIG_PRECISION must hold for the corresponding input arguments.
The condition all(0._RKG <= zig) must hold for the corresponding input arguments.
The condition size(zig, 1) == 2 must hold for the corresponding input arguments.
These conditions are verified only if the library is built with the preprocessor macro CHECK_ENABLED=1.
-
The
pure procedure(s) documented herein become impure when the ParaMonte library is compiled with preprocessor macro CHECK_ENABLED=1.
By default, these procedures are pure in release build and impure in debug and testing builds. The procedures of this generic interface are always impure when the input argument rng is missing.
- See also
- getNormRand
setNormRand
setNormRandBox
getNormLogPDF
getNormCDF
Example usage ⛓
12 integer(IK),
parameter :: NP
= 1000_IK
13 real(RK), dimension(NP) :: rand
15 type(display_type) :: disp
22 call disp%show(
"!%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%")
23 call disp%show(
"! Normal random number from a Standard Normal distribution.")
24 call disp%show(
"!%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%")
28 call disp%show(
"call setNormRand(rand(1))")
35 call disp%show(
"call setNormRand(rand(1:5))")
48 real(RK),
allocatable :: zig(:,:)
49 integer(IK) :: fileUnit, i
50 integer(IK),
parameter :: NP
= 10000_IK
51 real(RK), dimension(NP) :: rand1, rand2, rand3
53 call setNormRand(rand1, zig); rand1
= rand1
* 3.0_RK + 2._RK
54 call setNormRand(rand2, zig); rand2
= rand2
* 1.0_RK + 0._RK
55 call setNormRand(rand3); rand3
= rand3
* 1.0_RK - 5._RK
56 open(newunit
= fileUnit, file
= "setNormRand.RK.txt")
57 write(fileUnit,
"(3(g0,:,' '))") ( rand1(i)
&
Return the linSpace output argument with size(linSpace) elements of evenly-spaced values over the int...
Return the logSpace output argument with size(logSpace) elements of logarithmically-evenly-spaced val...
Generate and return the lower right edges of the rectangles of a Ziggurat partitioning of the Normal ...
This is a generic method of the derived type display_type with pass attribute.
This is a generic method of the derived type display_type with pass attribute.
This module contains procedures and generic interfaces for generating arrays with linear or logarithm...
This module contains classes and procedures for input/output (IO) or generic display operations on st...
type(display_type) disp
This is a scalar module variable an object of type display_type for general display.
This module defines the relevant Fortran kind type-parameters frequently used in the ParaMonte librar...
integer, parameter RK
The default real kind in the ParaMonte library: real64 in Fortran, c_double in C-Fortran Interoperati...
integer, parameter IK
The default integer kind in the ParaMonte library: int32 in Fortran, c_int32_t in C-Fortran Interoper...
integer, parameter SK
The default character kind in the ParaMonte library: kind("a") in Fortran, c_char in C-Fortran Intero...
Generate and return an object of type display_type.
Example Unix compile command via Intel ifort compiler ⛓
3ifort -fpp -standard-semantics -O3 -Wl,-rpath,../../../lib -I../../../inc main.F90 ../../../lib/libparamonte* -o main.exe
Example Windows Batch compile command via Intel ifort compiler ⛓
2set PATH=..\..\..\lib;%PATH%
3ifort /fpp /standard-semantics /O3 /I:..\..\..\include main.F90 ..\..\..\lib\libparamonte*.lib /exe:main.exe
Example Unix / MinGW compile command via GNU gfortran compiler ⛓
3gfortran -cpp -ffree-line-length-none -O3 -Wl,-rpath,../../../lib -I../../../inc main.F90 ../../../lib/libparamonte* -o main.exe
Example output ⛓
14-0.24646726760892629,
-0.11577041583496477,
+0.72691743029498113,
-1.3053477470218346,
+1.8072169383799661
Postprocessing of the example output ⛓
3import matplotlib.pyplot
as plt
16xlab = {
"CK" :
"Normal Random Number ( real/imaginary components )"
17 ,
"IK" :
"Normal Random Number ( integer-valued )"
18 ,
"RK" :
"Normal Random Number ( real-valued )"
20legends = [
r"$\mu = -5.,~\sigma = 1.0$"
21 ,
r"$\mu = 0.0,~\sigma = 1.0$"
22 ,
r"$\mu = 2.0,~\sigma = 3.0$"
25for kind
in [
"IK",
"CK",
"RK"]:
27 pattern =
"*." + kind +
".txt"
28 fileList = glob.glob(pattern)
29 if len(fileList) == 1:
31 df = pd.read_csv(fileList[0], delimiter =
" ", header =
None)
33 fig = plt.figure(figsize = 1.25 * np.array([6.4, 4.8]), dpi = 200)
37 plt.hist( df.values[:,0:3]
38 , histtype =
"stepfilled"
43 plt.hist( df.values[:,0:3]
44 , histtype =
"stepfilled"
51 plt.xticks(fontsize = fontsize - 2)
52 plt.yticks(fontsize = fontsize - 2)
53 ax.set_xlabel(xlab[kind], fontsize = 17)
54 ax.set_ylabel(
"Count", fontsize = 17)
55 ax.set_title(
"Histograms of {} Normal random numbers".format(len(df.values[:, 0])), fontsize = 17)
57 plt.grid(visible =
True, which =
"both", axis =
"both", color =
"0.85", linestyle =
"-")
58 ax.tick_params(axis =
"y", which =
"minor")
59 ax.tick_params(axis =
"x", which =
"minor")
61 plt.savefig(fileList[0].replace(
".txt",
".png"))
63 elif len(fileList) > 1:
65 sys.exit(
"Ambiguous file list exists.")
Visualization of the example output ⛓
- Benchmarks:
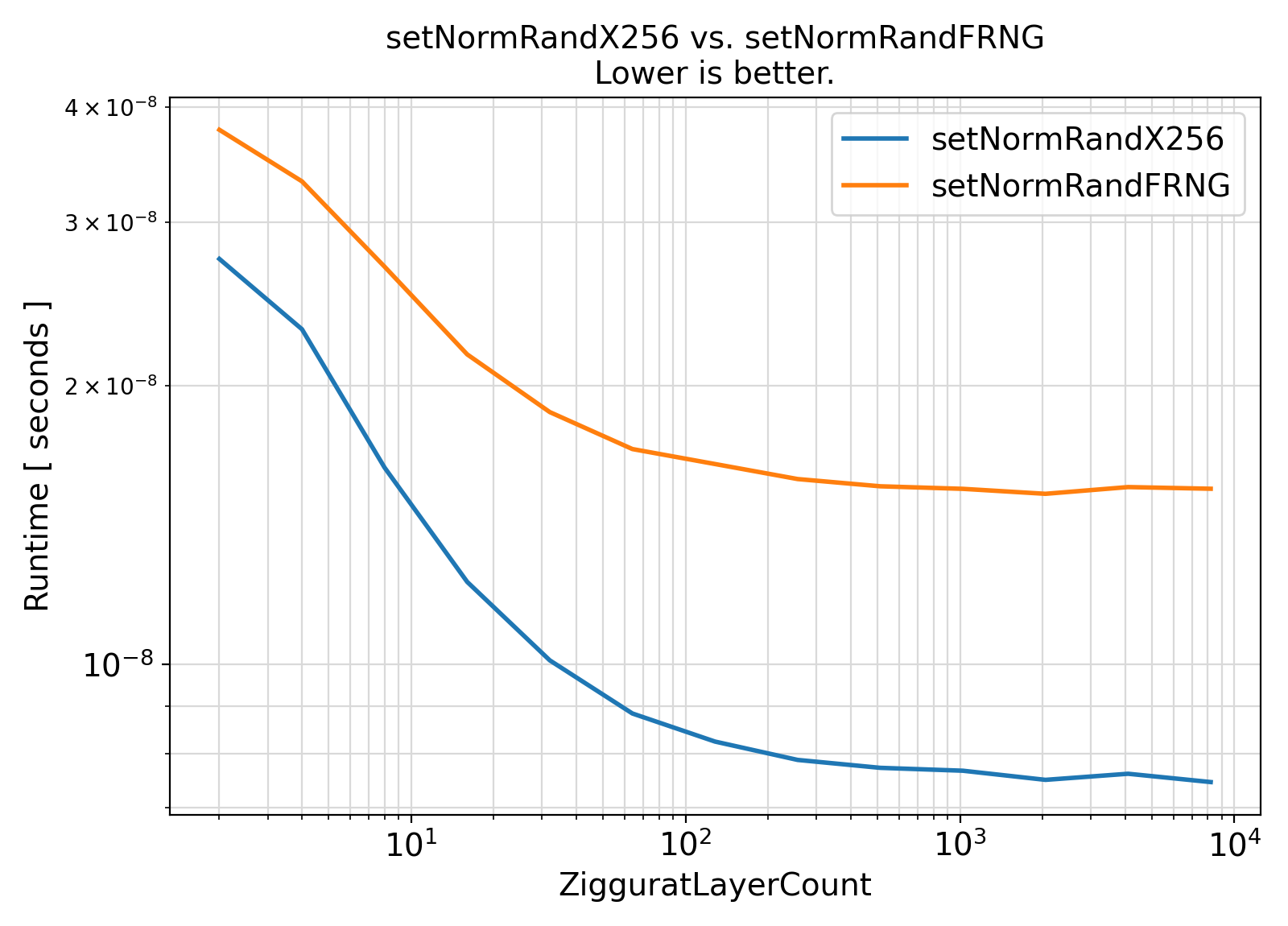
Benchmark :: The runtime performance of setNormRand for different implementations of the Box-Muller algorithm. ⛓
15 integer(IK) :: fileUnit
16 integer(IK) ,
parameter :: NSET
= 13_IK
17 integer(IK) ,
parameter :: NSIM
= 10000_IK
18 real(RKG) ,
allocatable :: zig(:,:)
19 real(RKG) :: rand(NSIM)
20 real(RKG) :: dummy
= 0._RKG
21 type(bench_type) ,
allocatable :: bench(:)
22 type(xoshiro256ssw_type) :: rng
24 rng
= xoshiro256ssw_type()
25 bench
= [
bench_type(name
= SK_
"setNormRandX256", exec
= setNormRandX256, overhead
= setOverhead)
&
26 ,
bench_type(name
= SK_
"setNormRandFRNG", exec
= setNormRandFRNG, overhead
= setOverhead)
&
29 open(newunit
= fileUnit, file
= "main.out", status
= "replace")
31 write(fileUnit,
"(*(g0,:,','))")
"ZigguratLayerCount", (bench(ibench)
%name, ibench
= 1,
size(bench))
33 loopOverZigSets:
do iset
= 1, NSET
37 write(
*,
"(*(g0,:,' '))")
"Benchmarking setNormRand() with ziggurat set size and abserr", nlay, dummy
38 do ibench
= 1,
size(bench)
39 bench(ibench)
%timing
= bench(ibench)
%getTiming(miniter
= 10_IK)
41 write(fileUnit,
"(*(g0,:,','))") nlay, (bench(ibench)
%timing
%mean
/ NSIM, ibench
= 1,
size(bench))
42 write(
*,
"(*(g0,:,' '))") dummy
44 end do loopOverZigSets
54 subroutine setOverhead()
59 dummy
= dummy
+ sum(rand)
62 subroutine setNormRandFRNG()
67 subroutine setNormRandX256()
Generate and return an object of type timing_type containing the benchmark timing information and sta...
This module contains abstract interfaces and types that facilitate benchmarking of different procedur...
This is the class for creating benchmark and performance-profiling objects.
Example Unix compile command via Intel ifort compiler ⛓
3ifort -fpp -standard-semantics -O3 -Wl,-rpath,../../../lib -I../../../inc main.F90 ../../../lib/libparamonte* -o main.exe
Example Windows Batch compile command via Intel ifort compiler ⛓
2set PATH=..\..\..\lib;%PATH%
3ifort /fpp /standard-semantics /O3 /I:..\..\..\include main.F90 ..\..\..\lib\libparamonte*.lib /exe:main.exe
Example Unix / MinGW compile command via GNU gfortran compiler ⛓
3gfortran -cpp -ffree-line-length-none -O3 -Wl,-rpath,../../../lib -I../../../inc main.F90 ../../../lib/libparamonte* -o main.exe
Postprocessing of the benchmark output ⛓
3import matplotlib.pyplot
as plt
8dirname = os.path.basename(os.getcwd())
12df = pd.read_csv(
"main.out", delimiter =
",")
13colnames = list(df.columns.values)
19ax = plt.figure(figsize = 1.25 * np.array([6.4,4.6]), dpi = 200)
22for colname
in colnames[1:]:
23 plt.plot( df[colnames[0]].values
28plt.xticks(fontsize = fontsize)
29plt.yticks(fontsize = fontsize)
30ax.set_xlabel(colnames[0], fontsize = fontsize)
31ax.set_ylabel(
"Runtime [ seconds ]", fontsize = fontsize)
32ax.set_title(
" vs. ".join(colnames[1:])+
"\nLower is better.", fontsize = fontsize)
36plt.grid(visible =
True, which =
"both", axis =
"both", color =
"0.85", linestyle =
"-")
37ax.tick_params(axis =
"y", which =
"minor")
38ax.tick_params(axis =
"x", which =
"minor")
39ax.legend ( colnames[1:]
46plt.savefig(
"benchmark." + dirname +
".runtime.png")
52ax = plt.figure(figsize = 1.25 * np.array([6.4,4.6]), dpi = 200)
55for colname
in colnames[1:]:
56 plt.plot( df[colnames[0]].values
57 , df[colname].values / df[colnames[1]].values.min()
61plt.xticks(fontsize = fontsize)
62plt.yticks(fontsize = fontsize)
63ax.set_xlabel(colnames[0], fontsize = fontsize)
64ax.set_ylabel(
"Runtime compared to the fastest {}.".format(colnames[1]), fontsize = fontsize)
65ax.set_title(
"Runtime Ratio Comparison. Lower means faster.\nLower than 1 means faster than the fastest {}() run.".format(colnames[1]), fontsize = fontsize)
69plt.grid(visible =
True, which =
"both", axis =
"both", color =
"0.85", linestyle =
"-")
70ax.tick_params(axis =
"y", which =
"minor")
71ax.tick_params(axis =
"x", which =
"minor")
72ax.legend ( colnames[1:]
79plt.savefig(
"benchmark." + dirname +
".runtime.ratio.png")
Visualization of the benchmark output ⛓
Benchmark moral ⛓
- The benchmark procedures named
setNormRandX256 and setNormRandFRNG call the generic interface setNormRand to generate Normal random values via Ziggurat algorithm with the Xoshiro256** and the intrinsic Fortran Uniform RNG, respectively.
This benchmark confirms the popular choice of the number of 256 Ziggurat layers as the optimal value.
Nevertheless, the benchmarks appear to show improvements with even larger number of Ziggurat layers, depending on the platform, processor, and compiler choice.
- Test:
- test_pm_distNorm
Final Remarks ⛓
If you believe this algorithm or its documentation can be improved, we appreciate your contribution and help to edit this page's documentation and source file on GitHub.
For details on the naming abbreviations, see this page.
For details on the naming conventions, see this page.
This software is distributed under the MIT license with additional terms outlined below.
-
If you use any parts or concepts from this library to any extent, please acknowledge the usage by citing the relevant publications of the ParaMonte library.
-
If you regenerate any parts/ideas from this library in a programming environment other than those currently supported by this ParaMonte library (i.e., other than C, C++, Fortran, MATLAB, Python, R), please also ask the end users to cite this original ParaMonte library.
This software is available to the public under a highly permissive license.
Help us justify its continued development and maintenance by acknowledging its benefit to society, distributing it, and contributing to it.
- Copyright
- Computational Data Science Lab
- Author:
- Amir Shahmoradi, Oct 16, 2009, 11:14 AM, Michigan
Definition at line 2022 of file pm_distNorm.F90.