Compute and return an asymptotically optimal set of cluster centers for the input sample, cluster membership IDs, and sample distances-squared from their corresponding cluster centers.
More...
Compute and return an asymptotically optimal set of cluster centers for the input sample, cluster membership IDs, and sample distances-squared from their corresponding cluster centers.
See the documentation of pm_clusKmeans for more information on the Kmeans++ clustering algorithm.
The metric used within this generic interface is the Euclidean distance.
- Parameters
-
| [in,out] | rng | : The input/output scalar that can be an object of,
-
type rngf_type, implying the use of intrinsic Fortran uniform RNG.
-
type xoshiro256ssw_type, implying the use of xoshiro256** uniform RNG.
|
| [out] | membership | : The output vector of shape (1:nsam) of type integer of default kind IK, containing the membership of each input sample in sample from its nearest cluster center, such that cluster(membership(i)) is the nearest cluster center to the ith sample sample(:, i) at a squared-distance of disq(i).
|
| [out] | disq | : The output vector of shape (1:nsam) of the same type and kind as the input argument sample, containing the Euclidean squared distance of each input sample in sample from its nearest cluster center.
|
| [out] | csdisq | : The output vector of shape (1:nsam+1) of the same type and kind as the input argument sample, containing the cumulative sum of the Euclidean squared distance of each input sample in sample from its nearest cluster center.
While the output contents are mostly useless, this argument can aid the algorithm efficiency to resolving the need for internal space allocation.
This potential speed-up is particularly relevant when the procedure is called repeatedly many times on samples of the same size.
|
| [in] | sample | : The input vector, or matrix of,
-
type
real of kind any supported by the processor (e.g., RK, RK32, RK64, or RK128),
containing the sample of nsam points in a ndim-dimensional space whose corresponding cluster centers must be computed.
-
If
sample is a vector of shape (1 : nsam) and center is a vector of shape (1 : ncls), then the input sample must be a collection of nsam points (in univariate space).
-
If
sample is a matrix of shape (1 : ndim, 1 : nsam) and center is a matrix of shape (1 : ndim, 1 : ncls), then the input sample must be a collection of nsam points (in ndim-dimensional space).
|
| [in] | ncls | : The input scalar of type integer of default kind IK, containing the number of the desired clusters to be identified in the sample.
(optional, default = ubound(center, 2). It must be present if and only if the output arguments center, size, and potential are all missing.) |
| [out] | center | : The output vector of shape (1:ncls) or matrix of shape (1 : ndim, 1 : ncls) of the same type and kind as the input argument sample, containing the set of ncls unique random cluster centers (centroids) selected from the input sample based on the computed memberships and minimum sample-cluster distances disq.
(optional. If missing, no cluster center information will be output.) |
| [out] | size | : The output vector of shape (1:ncls) type integer of default kind IK, containing the sizes (number of members) of the clusters with the corresponding centers output in the argument center.
(optional. If missing, no cluster size information will be output.) |
| [out] | potential | : The output vector of shape (1:ncls) of the same type and kind as the input argument sample, the ith element of which contains the sum of squared distances of all members of the ith cluster from the cluster center as output in the ith element of center.
(optional. If missing, no cluster potential information will be output.) |
Possible calling interfaces ⛓
call setKmeansPP(rng, membership(
1 : nsam), disq(
1 : nsam), csdisq(
0 : nsam), sample(
1 : ndim,
1 : nsam), ncls)
call setKmeansPP(rng, membership(
1 : nsam), disq(
1 : nsam), csdisq(
0 : nsam), sample(
1 : ndim,
1 : nsam), center(
1 : ndim,
1 : ncls),
size(
1 : ncls), potential(
1 : ncls))
Compute and return an asymptotically optimal set of cluster centers for the input sample,...
This module contains procedures and routines for the computing the Kmeans clustering of a given set o...
- Warning
- The condition
ubound(center, rank(center)) > 0 must hold for the corresponding input arguments.
The condition ubound(sample, rank(sample)) == size(disq, 1) must hold for the corresponding input arguments.
The condition ubound(sample, rank(sample)) == size(csdisq, 1) - 1 must hold for the corresponding input arguments.
The condition ubound(center, rank(center)) == size(size, 1) must hold for the corresponding input arguments.
The condition ubound(center, rank(center)) == size(potential, 1) must hold for the corresponding input arguments.
The condition ubound(sample, rank(sample)) == size(membership, 1) must hold for the corresponding input arguments.
The condition ubound(center, rank(center)) <= size(sample, rank(sample)) must hold for the corresponding input arguments (the number of clusters must be less than or equal to the sample size).
The condition ubound(sample, 1) == ubound(center, 1) must hold for the corresponding input arguments.
These conditions are verified only if the library is built with the preprocessor macro CHECK_ENABLED=1.
-
By definition, the number of points in the input
sample must be larger than the specified number of clusters.
-
The
pure procedure(s) documented herein become impure when the ParaMonte library is compiled with preprocessor macro CHECK_ENABLED=1.
By default, these procedures are pure in release build and impure in debug and testing builds. The procedures of this generic interface are always impure when the input rng argument is set to an object of type rngf_type.
- Note
- Dropping the optional arguments can aid runtime performance.
This is particularly relevant when the output of this generic interface is directly passed to the k-means algorithm.
- See also
- setKmeans
setCenter
setMember
setKmeansPP
Arthur, D.; Vassilvitskii, S. (2007). k-means++: the advantages of careful seeding
Example usage ⛓
12 integer(IK) :: ndim, nsam, ncls, itry
13 real(RKG) ,
allocatable :: sample(:,:), center(:,:), disq(:), csdisq(:), potential(:)
14 integer(IK) ,
allocatable :: membership(:),
size(:)
15 type(display_type) :: disp
20 call disp%show(
"!%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%")
21 call disp%show(
"! Compute cluster centers based on an input sample and cluster memberships and member-center distances.")
22 call disp%show(
"!%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%")
27 call disp%show(
"ndim = getUnifRand(1, 5); ncls = getUnifRand(1, 5); nsam = getUnifRand(ncls, 2 * ncls);")
31 call disp%show(
"sample = getUnifRand(0., 5., ndim, nsam) ! Create a random sample.")
35 call disp%show(
"call setResized(disq, nsam)")
37 call disp%show(
"call setResized(csdisq, nsam + 1_IK)")
39 call disp%show(
"call setResized(membership, nsam)")
41 call disp%show(
"call setResized(center, [ndim, ncls])")
43 call disp%show(
"call setResized(potential, ncls)")
45 call disp%show(
"call setResized(size, ncls)")
49 call disp%show(
"call setKmeansPP(rngf, membership, disq, csdisq, sample, center, size, potential) ! compute the new clusters and memberships.")
50 call setKmeansPP(
rngf, membership, disq, csdisq, sample, center, size, potential)
71 integer(IK) :: funit, i
83 call setKmeansPP(
rngf, membership, disq, csdisq, sample, center, size, potential)
84 open(newunit
= funit, file
= "setKmeansPP.center.txt")
86 write(funit,
"(*(g0,:,','))") i, center(:,i)
89 open(newunit
= funit, file
= "setKmeansPP.sample.txt")
91 write(funit,
"(*(g0,:,','))") membership(i), sample(:,i)
Allocate or resize (shrink or expand) an input allocatable scalar string or array of rank 1....
Generate and return a scalar or a contiguous array of rank 1 of length s1 of randomly uniformly distr...
This is a generic method of the derived type display_type with pass attribute.
This is a generic method of the derived type display_type with pass attribute.
This module contains procedures and generic interfaces for resizing allocatable arrays of various typ...
This module contains classes and procedures for computing various statistical quantities related to t...
type(rngf_type) rngf
The scalar constant object of type rngf_type whose presence signified the use of the Fortran intrinsi...
This module contains classes and procedures for input/output (IO) or generic display operations on st...
type(display_type) disp
This is a scalar module variable an object of type display_type for general display.
This module defines the relevant Fortran kind type-parameters frequently used in the ParaMonte librar...
integer, parameter LK
The default logical kind in the ParaMonte library: kind(.true.) in Fortran, kind(....
integer, parameter IK
The default integer kind in the ParaMonte library: int32 in Fortran, c_int32_t in C-Fortran Interoper...
integer, parameter SK
The default character kind in the ParaMonte library: kind("a") in Fortran, c_char in C-Fortran Intero...
integer, parameter RKS
The single-precision real kind in Fortran mode. On most platforms, this is an 32-bit real kind.
Generate and return an object of type display_type.
Example Unix compile command via Intel ifort compiler ⛓
3ifort -fpp -standard-semantics -O3 -Wl,-rpath,../../../lib -I../../../inc main.F90 ../../../lib/libparamonte* -o main.exe
Example Windows Batch compile command via Intel ifort compiler ⛓
2set PATH=..\..\..\lib;%PATH%
3ifort /fpp /standard-semantics /O3 /I:..\..\..\include main.F90 ..\..\..\lib\libparamonte*.lib /exe:main.exe
Example Unix / MinGW compile command via GNU gfortran compiler ⛓
3gfortran -cpp -ffree-line-length-none -O3 -Wl,-rpath,../../../lib -I../../../inc main.F90 ../../../lib/libparamonte* -o main.exe
Example output ⛓
12+2.13936520,
+2.17753863,
+0.947716832,
+2.24455094,
+2.49617219,
+4.08531094
13+0.651172996,
+4.58386707,
+4.13581896,
+0.258072019,
+3.09623241,
+4.53492117
14+2.17715549,
+0.703817308,
+1.67591071,
+4.84981823,
+0.341176987E-2,
+0.323704481
15+3.63314629,
+4.74875069,
+4.84903622,
+2.16089058,
+2.26878262,
+2.55698085
23call setKmeansPP(
rngf, membership, disq, csdisq, sample, center, size, potential)
25+0.00000000,
+2.66823173,
+0.00000000,
+0.00000000,
+4.78083277,
+0.00000000
27+0.00000000,
+0.00000000,
+8.59033203,
+23.8827496,
+23.8827496,
+28.6635818,
+28.6635818
31+4.78083277,
+0.00000000,
+0.00000000,
+2.66823173
33+4.08531094,
+2.13936520,
+2.24455094,
+0.947716832
34+4.53492117,
+0.651172996,
+0.258072019,
+4.13581896
35+0.323704481,
+2.17715549,
+4.84981823,
+1.67591071
36+2.55698085,
+3.63314629,
+2.16089058,
+4.84903622
46+2.59935498,
+2.73426986
47+2.57192349,
+0.270605683
48+4.94351578,
+4.36086369
56call setKmeansPP(
rngf, membership, disq, csdisq, sample, center, size, potential)
58+0.00000000,
+0.00000000
60+0.00000000,
+0.00000000,
+5.65374804
64+0.00000000,
+0.00000000
66+2.59935498,
+2.73426986
67+2.57192349,
+0.270605683
68+4.94351578,
+4.36086369
78+4.35638189,
+2.88354635,
+4.50853157,
+2.91200066
79+0.780458748,
+2.55000567,
+4.34746838,
+2.98939347
80+3.27596521,
+1.86596012,
+4.73504066,
+3.28873634
81+0.755269527,
+3.99303579,
+2.21679306,
+4.70031929
89call setKmeansPP(
rngf, membership, disq, csdisq, sample, center, size, potential)
91+0.00000000,
+0.00000000,
+0.00000000,
+0.00000000
93+0.00000000,
+0.00000000,
+0.00000000,
+0.00000000,
+2.71841335
97+0.00000000,
+0.00000000,
+0.00000000,
+0.00000000
99+4.50853157,
+2.88354635,
+4.35638189,
+2.91200066
100+4.34746838,
+2.55000567,
+0.780458748,
+2.98939347
101+4.73504066,
+1.86596012,
+3.27596521,
+3.28873634
102+2.21679306,
+3.99303579,
+0.755269527,
+4.70031929
112+4.24514055,
+0.897808373,
+0.927564502,
+3.35978222,
+4.77875185,
+0.634441078
113+4.65616798,
+1.51281857,
+1.44810057,
+3.76173306,
+2.64224172,
+1.65918112
114+0.345850587,
+4.36776066,
+3.06332016,
+1.13277137,
+4.39145947,
+2.38435626
122call setKmeansPP(
rngf, membership, disq, csdisq, sample, center, size, potential)
124+0.00000000,
+0.00000000,
+1.70663893,
+2.20311761,
+0.00000000,
+4.02467728
126+0.00000000,
+0.00000000,
+0.00000000,
+1.70663893,
+3.90975666,
+20.2476349,
+24.2723122
128+1,
+2,
+2,
+1,
+3,
+2
130+2.20311761,
+5.73131609,
+0.00000000
132+4.24514055,
+0.897808373,
+4.77875185
133+4.65616798,
+1.51281857,
+2.64224172
134+0.345850587,
+4.36776066,
+4.39145947
144+2.47468925,
+3.65329885,
+2.77629018,
+2.35368824,
+4.87198305,
+0.579373837,
+0.306171477
145+3.19468379,
+1.44800127,
+0.577837527,
+2.03795338,
+3.27591443,
+0.616323948E-1,
+0.865943432
146+0.283397734,
+2.40631151,
+0.382784009,
+4.38773918,
+2.25751114,
+3.19946575,
+3.87321019
147+0.704022348,
+4.14455366,
+3.30926275,
+4.21819019,
+0.974922180,
+1.09258795,
+2.93798327
155call setKmeansPP(
rngf, membership, disq, csdisq, sample, center, size, potential)
157+0.00000000,
+6.31870413,
+0.00000000,
+7.46960211,
+0.00000000,
+4.58097124,
+0.00000000
159+0.00000000,
+9.72412682,
+16.0428314,
+16.0428314,
+23.5124340,
+23.5124340,
+28.0934048,
+28.0934048
161+4,
+3,
+3,
+1,
+2,
+1,
+1
163+12.0505733,
+0.00000000,
+6.31870413,
+0.00000000
165+0.306171477,
+4.87198305,
+2.77629018,
+2.47468925
166+0.865943432,
+3.27591443,
+0.577837527,
+3.19468379
167+3.87321019,
+2.25751114,
+0.382784009,
+0.283397734
168+2.93798327,
+0.974922180,
+3.30926275,
+0.704022348
189call setKmeansPP(
rngf, membership, disq, csdisq, sample, center, size, potential)
193+0.00000000,
+0.00000000
212+4.59279203,
+3.36288404,
+4.68041801,
+3.04189396
213+3.75420284,
+0.365414619,
+2.62552929,
+1.73626685
214+4.54929590,
+2.66871405,
+2.92258310,
+2.53342366
215+2.00651026,
+1.38389969,
+1.00021958,
+4.89269209
216+2.82053685,
+2.90131426,
+2.05227757,
+1.54346645
224call setKmeansPP(
rngf, membership, disq, csdisq, sample, center, size, potential)
226+5.53062010,
+0.00000000,
+0.00000000,
+16.1559486
228+0.00000000,
+5.53062010,
+13.3071575,
+13.3071575,
+32.3443832
232+5.53062010,
+16.1559486
234+4.68041801,
+3.36288404
235+2.62552929,
+0.365414619
236+2.92258310,
+2.66871405
237+1.00021958,
+1.38389969
238+2.05227757,
+2.90131426
259call setKmeansPP(
rngf, membership, disq, csdisq, sample, center, size, potential)
263+0.00000000,
+0.00000000
282+3.24985957,
+2.60311246,
+4.29312801,
+2.91351557,
+3.01679873,
+1.15002632,
+1.67796826,
+1.60555029
290call setKmeansPP(
rngf, membership, disq, csdisq, sample, center, size, potential)
292+0.113127291,
+0.00000000,
+0.00000000,
+0.00000000,
+0.106674125E-1,
+0.278722703,
+0.00000000,
+0.524436310E-2
294+0.00000000,
+0.113127291,
+0.209477380,
+0.209477380,
+0.209477380,
+0.220144793,
+0.498867512,
+0.498867512,
+0.504111886
296+1,
+4,
+3,
+1,
+1,
+2,
+2,
+2
298+0.123794705,
+0.283967078,
+0.00000000,
+0.00000000
300+2.91351557,
+1.67796826,
+4.29312801,
+2.60311246
310+0.919935107,
+3.98182631
311+3.51151609,
+3.49986529
312+4.04880810,
+4.76683187
320call setKmeansPP(
rngf, membership, disq, csdisq, sample, center, size, potential)
322+0.00000000,
+9.89087105
324+0.00000000,
+0.00000000,
+9.89087105
Postprocessing of the example output ⛓
3import matplotlib.pyplot
as plt
11fig = plt.figure(figsize = 1.25 * np.array([6.4, 4.8]), dpi = 200)
14parent = os.path.basename(os.path.dirname(__file__))
15pattern = parent +
"*.txt"
17fileList = glob.glob(pattern)
22 kind = file.split(
".")[1]
23 prefix = file.split(
".")[0]
24 df = pd.read_csv(file, delimiter =
",", header =
None)
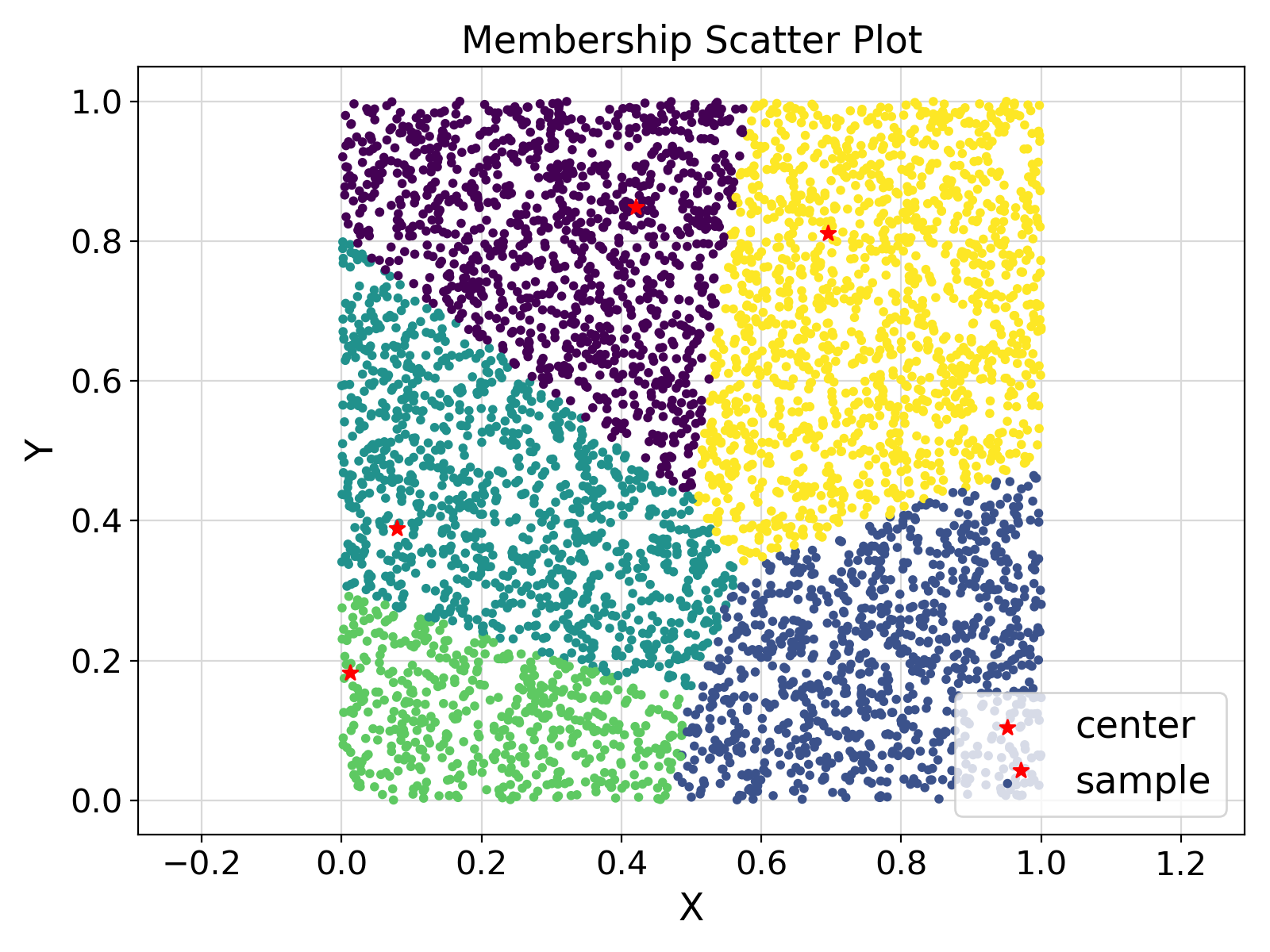
27 ax.scatter ( df.values[:, 1]
34 legends.append(
"center")
35 elif kind ==
"sample":
36 ax.scatter ( df.values[:, 1]
41 legends.append(
"sample")
43 sys.exit(
"Ambiguous file exists: {}".format(file))
45 ax.legend(legends, fontsize = fontsize)
46 plt.xticks(fontsize = fontsize - 2)
47 plt.yticks(fontsize = fontsize - 2)
48 ax.set_xlabel(
"X", fontsize = 17)
49 ax.set_ylabel(
"Y", fontsize = 17)
50 ax.set_title(
"Membership Scatter Plot", fontsize = fontsize)
53 plt.grid(visible =
True, which =
"both", axis =
"both", color =
"0.85", linestyle =
"-")
54 ax.tick_params(axis =
"y", which =
"minor")
55 ax.tick_params(axis =
"x", which =
"minor")
56 ax.set_axisbelow(
True)
59 plt.savefig(prefix +
".png")
61 sys.exit(
"Ambiguous file list exists.")
Visualization of the example output ⛓
- Test:
- test_pm_clusKmeans
Final Remarks ⛓
If you believe this algorithm or its documentation can be improved, we appreciate your contribution and help to edit this page's documentation and source file on GitHub.
For details on the naming abbreviations, see this page.
For details on the naming conventions, see this page.
This software is distributed under the MIT license with additional terms outlined below.
-
If you use any parts or concepts from this library to any extent, please acknowledge the usage by citing the relevant publications of the ParaMonte library.
-
If you regenerate any parts/ideas from this library in a programming environment other than those currently supported by this ParaMonte library (i.e., other than C, C++, Fortran, MATLAB, Python, R), please also ask the end users to cite this original ParaMonte library.
This software is available to the public under a highly permissive license.
Help us justify its continued development and maintenance by acknowledging its benefit to society, distributing it, and contributing to it.
- Copyright
- Computational Data Science Lab If you use or redistribute ideas based on this generic interface implementation, you should also cite the original k-means++ article:
Arthur, D.; Vassilvitskii, S. (2007). k-means++: the advantages of careful seeding
- Author:
- Amir Shahmoradi, September 1, 2012, 12:00 AM, National Institute for Fusion Studies, The University of Texas Austin
Definition at line 1181 of file pm_clusKmeans.F90.