
|
ParaMonte Fortran 2.0.0
Parallel Monte Carlo and Machine Learning Library
See the latest version documentation. |

|
ParaMonte Fortran 2.0.0
Parallel Monte Carlo and Machine Learning Library
See the latest version documentation. |
Compute and return an iteratively-refined set of cluster centers given the input sample using the k-means approach.
More...
Compute and return an iteratively-refined set of cluster centers given the input sample using the k-means approach.
See the documentation of pm_clusKmeans for more information on the Kmeans clustering algorithm.
The metric used within this generic interface is the Euclidean distance.
| [in,out] | rng | : The input/output scalar that can be an object of,
intent(inout) arguments below have intent(out) argument and will be initialized using the k-means++ algorithm.If this argument is missing, then the user must initialize all of the following arguments with intent(inout) via k-means++ or any other method before passing them to this generic interface.) |
| [in,out] | membership | : The input/output vector of shape (1:nsam) of type integer of default kind IK, containing the membership of each input sample in sample from its nearest cluster center, such that cluster(membership(i)) is the nearest cluster center to the ith sample sample(:, i) at a squared-distance of disq(i).If the argument rng is missing, then membership has intent(inout) and must be properly initialized before calling this routine.If the argument rng is present, then membership has intent(out) and will contain the final cluster memberships on output. |
| [in,out] | disq | : The input/output vector of shape (1:nsam) of the same type and kind as the input argument sample, containing the Euclidean squared distance of each input sample in sample from its nearest cluster center.If the argument rng is missing, then disq has intent(inout) and must be properly initialized before calling this routine.If the argument rng is present, then disq has intent(out) and will contain the final squared-distances from cluster centers on output. |
| [in] | sample | : The input vector, or matrix of,
containing the sample of nsam points in a ndim-dimensional space whose corresponding cluster centers must be computed.
|
| [in,out] | center | : The input/output vector of shape (1:ncls) or matrix of shape (1 : ndim, 1 : ncls) of the same type and kind as the input argument sample, containing the set of ncls unique cluster centers (centroids) computed based on the input sample memberships and minimum distances.If the argument rng is missing, then center has intent(inout) and must be properly initialized before calling this routine.If the argument rng is present, then center has intent(out) and will contain the final cluster centers on output. |
| [in,out] | size | : The input/output vector of shape (1:ncls) type integer of default kind IK, containing the sizes (number of members) of the clusters with the corresponding centers output in the argument center.If the argument rng is missing, then size has intent(inout) and must be properly initialized before calling this routine.If the argument rng is present, then size has intent(out) and will contain the final cluster sizes (member counts) on output. |
| [in,out] | potential | : The input/output vector of shape (1:ncls) of the same type and kind as the input argument sample, the ith element of which contains the sum of squared distances of all members of the ith cluster from the cluster center as output in the ith element of center.If the argument rng is missing, then potential has intent(inout) and must be properly initialized before calling this routine (although its values are not explicitly referenced).If the argument rng is present, then potential has intent(out) and will contain the final cluster potentials (sums of squared distances from cluster centers) on output. |
| [out] | failed | : The output scalar of type logical of default kind LK that is .true. if and only if the algorithm fails to converge within the user-specified or default criteria for convergence.Failure occurs only if any(size < minsize) .or. maxniter < niter. |
| [out] | niter | : The output scalar of type integer of default kind IK, containing the number of refinement iterations performed within the algorithm to achieve convergence.An output niter value larger than the input maxniter implies lack of convergence before return.(optional. If missing, the number of refinement iterations will not be output.) |
| [in] | maxniter | : The input non-negative scalar of type integer of default kind IK, containing the maximum number of refinement iterations allowed within the algorithm to achieve convergence.If convergence does not occur within the maximum specified value, the output arguments can be passed again as is to the generic interface (without the optional rng argument) to continue the refinement iterations until convergence.A reasonable choice can be 300 or comparable values.(optional, default = 300.) |
| [in] | minsize | : The input non-negative scalar of type integer of default kind IK, containing the minimum allowed size of each cluster.If any cluster has any number of members below the specified minsize, the algorithm will return without achieving convergence.The situation can be detected of any element of the output size is smaller than the specified minsize.A reasonable choice can be ndim = ubound(sample, 1) or comparable values although any non-negative value including zero is possible.(optional, default = 1.) |
| [in] | nfail | : The input non-negative scalar of type integer of default kind IK, containing the number of times the k-means algorithm is allowed to fail before returning without convergence.(optional. It can be present only if the argument rng is also present, allowing random initializations in case of failures.) |
Possible calling interfaces ⛓
rng is present, then all arguments associated with setKmeansPP equally apply to this generic interface.ubound(center, rank(center)) > 0 must hold for the corresponding input arguments.ubound(sample, rank(sample)) == ubound(disq, 1) must hold for the corresponding input arguments.ubound(center, rank(center)) == ubound(size, 1) must hold for the corresponding input arguments.ubound(center, rank(center)) == ubound(potential, 1) must hold for the corresponding input arguments.ubound(sample, rank(sample)) == ubound(membership, 1) must hold for the corresponding input arguments.ubound(center, rank(center)) <= ubound(sample, rank(sample)) must hold for the corresponding input arguments (the number of clusters must be less than or equal to the sample size).ubound(sample, 1) == ubound(center, 1) must hold for the corresponding input arguments.0 <= maxniter must hold for the corresponding input arguments.0 <= minsize must hold for the corresponding input arguments.0 <= nfail must hold for the corresponding input arguments.CHECK_ENABLED=1.pure procedure(s) documented herein become impure when the ParaMonte library is compiled with preprocessor macro CHECK_ENABLED=1.pure in release build and impure in debug and testing builds. The procedures of this generic interface are always impure when the input rng argument is set to an object of type rngf_type.
Example usage ⛓
ifort compiler ⛓ ifort compiler ⛓ gfortran compiler ⛓ 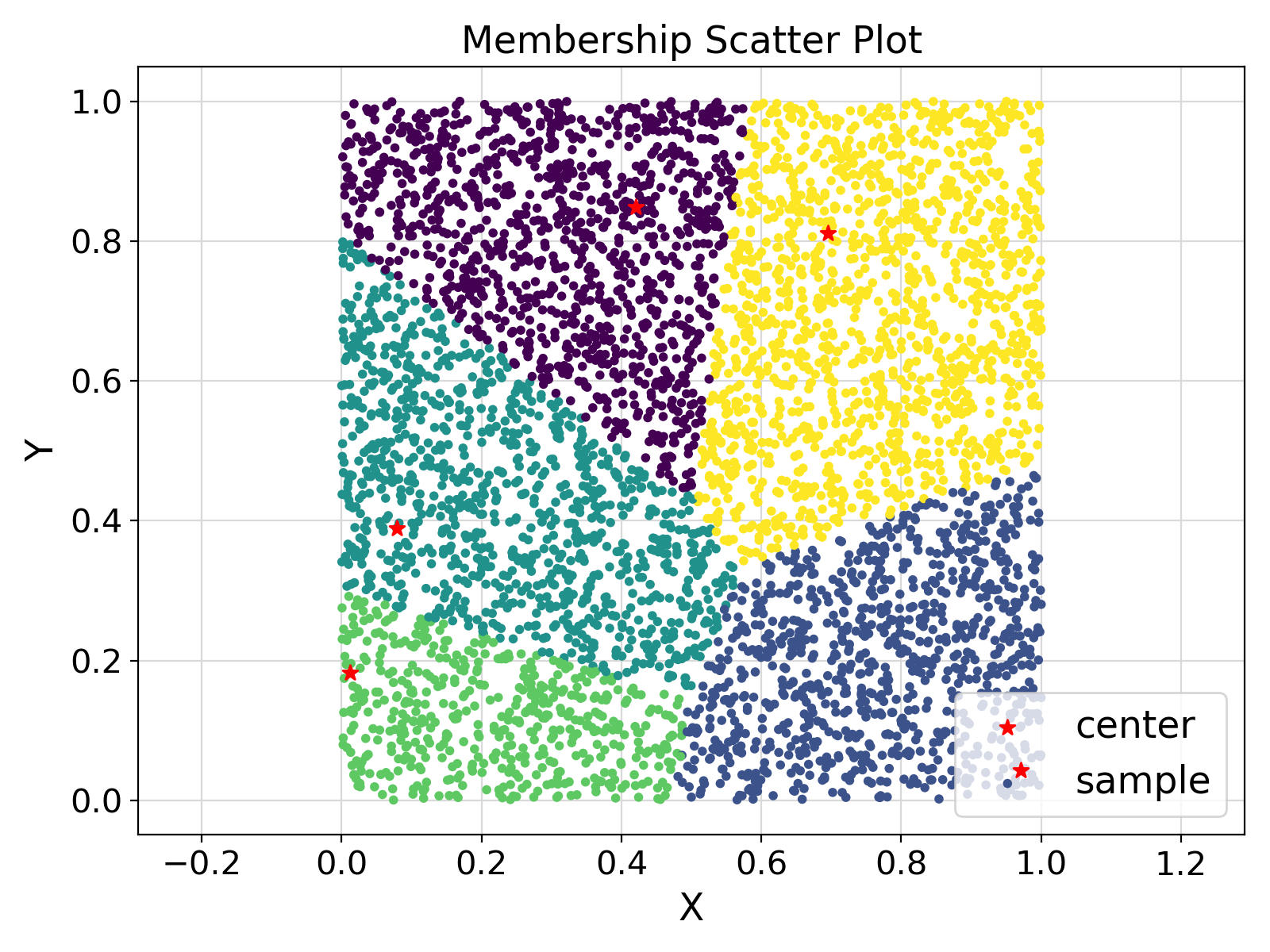
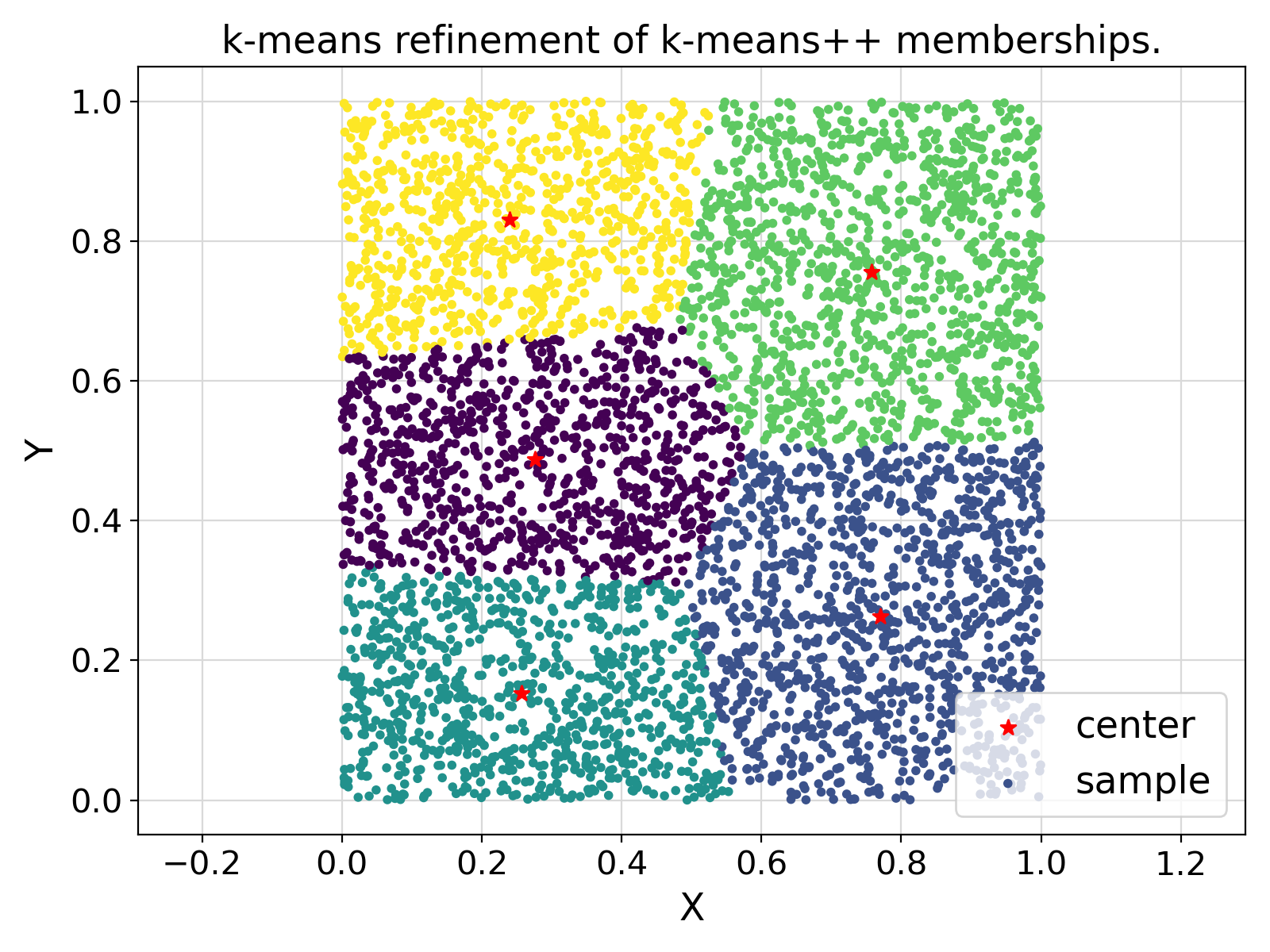
Final Remarks ⛓
If you believe this algorithm or its documentation can be improved, we appreciate your contribution and help to edit this page's documentation and source file on GitHub.
For details on the naming abbreviations, see this page.
For details on the naming conventions, see this page.
This software is distributed under the MIT license with additional terms outlined below.
This software is available to the public under a highly permissive license.
Help us justify its continued development and maintenance by acknowledging its benefit to society, distributing it, and contributing to it.
Definition at line 1661 of file pm_clusKmeans.F90.