Generate and return the inverse Fisher transformation of the input Fisher z value.
More...
Generate and return the inverse Fisher transformation of the input Fisher z value.
See the documentation of pm_mathFisher for information about the Fisher transformation.
- Parameters
-
| [in] | fisherz | : The input scalar (or array of the same shape as other array-like arguments) of,
-
type
real of kind any supported by the processor (e.g., RK, RK32, RK64, or RK128),
containing the Fisher z value(s). |
| [in] | lb | : The input scalar (or array of the same shape as other array-like arguments) of the same type and kind as fisherz, containing the lower bound of the range of the output val. (optional, default = -1. It must be present if and only if the optional input argument ub is also present.) |
| [in] | ub | : The input scalar (or array of the same shape as other array-like arguments) of the same type and kind as fisherz, containing the upper bound of the range of the output val. (optional, default = +1. It must be present if and only if the optional input argument lb is also present.) |
- Returns
val : The output scalar (or array of the same shape as other array-like arguments) of the same type and kind as fisherz, containing the result of the inverse Fisher transformation of the input fisherz.
Possible calling interfaces ⛓
Generate and return the inverse Fisher transformation of the input Fisher z value.
This module contains procedures and generic interfaces for evaluating the Fisher transformation and i...
- Warning
- The condition
lb < ub must hold for the corresponding input arguments.
This condition is verified only if the library is built with the preprocessor macro CHECK_ENABLED=1.
-
The
pure procedure(s) documented herein become impure when the ParaMonte library is compiled with preprocessor macro CHECK_ENABLED=1.
By default, these procedures are pure in release build and impure in debug and testing builds. The procedures of this generic interface are always pure when both optional arguments lb and ub are missing.
- See also
- getFisher
getFisherInv
Example usage ⛓
12 type(display_type) :: disp
13 real(RKG) :: redshift
= 5.5_RKG
17 call disp%show(
"!%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%")
18 call disp%show(
"!Compute the Inverse Fisher z transformation of a random bounded variable.")
19 call disp%show(
"!%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%")
24 real(RKG),
allocatable :: rand(:)
26 call disp%show(
"rand = getUnifRand(-9, 9, 5_IK)")
32 call disp%show(
"getFisherInv(rand, lb = -1._RKG, ub = 1._RKG)")
34 call disp%show(
"getFisherInv(rand, lb = 0._RKG, ub = 1._RKG)")
43 real(RKG),
allocatable :: fish(:)
45 if (
0 /= getErrTableWrite(
"getFisherInv.csv",
reshape([fish,
getFisherInv(fish)], [
size(fish),
2]), header
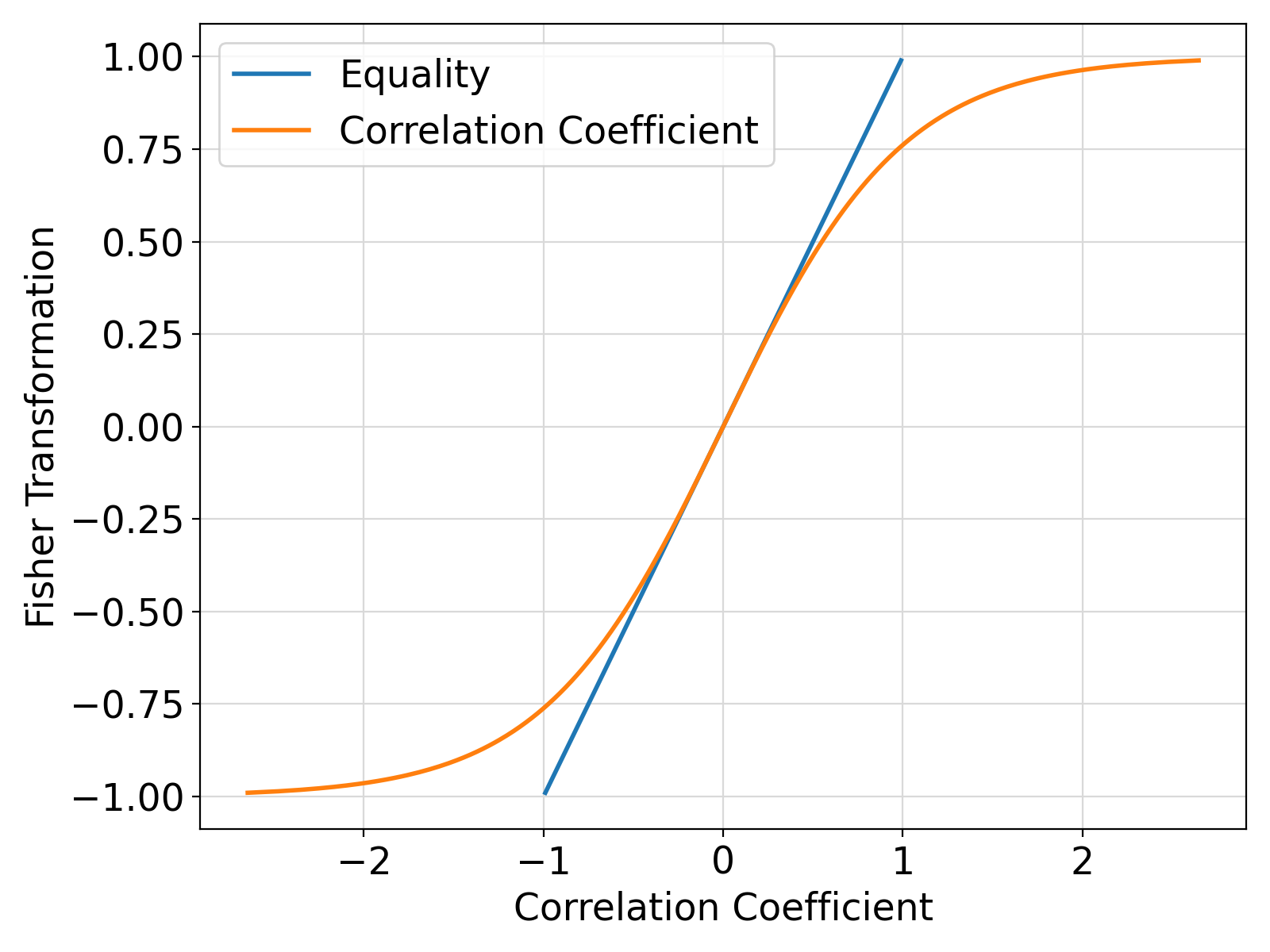
= "Fisher Transformation,Correlation Coefficient"))
error stop "Table writing failed."
Generate count evenly spaced points over the interval [x1, x2] if x1 < x2, or [x2,...
Generate and return a scalar or a contiguous array of rank 1 of length s1 of randomly uniformly distr...
Generate and return the iostat code resulting from writing the input table of rank 1 or 2 to the spec...
This is a generic method of the derived type display_type with pass attribute.
This is a generic method of the derived type display_type with pass attribute.
Generate and return the Fisher transformation of the input Fisher z value.
This module contains procedures and generic interfaces for generating arrays with linear or logarithm...
This module contains classes and procedures for computing various statistical quantities related to t...
This module contains classes and procedures for input/output (IO) or generic display operations on st...
type(display_type) disp
This is a scalar module variable an object of type display_type for general display.
This module defines the relevant Fortran kind type-parameters frequently used in the ParaMonte librar...
integer, parameter LK
The default logical kind in the ParaMonte library: kind(.true.) in Fortran, kind(....
integer, parameter IK
The default integer kind in the ParaMonte library: int32 in Fortran, c_int32_t in C-Fortran Interoper...
integer, parameter RKD
The double precision real kind in Fortran mode. On most platforms, this is an 64-bit real kind.
integer, parameter SK
The default character kind in the ParaMonte library: kind("a") in Fortran, c_char in C-Fortran Intero...
integer, parameter RKS
The single-precision real kind in Fortran mode. On most platforms, this is an 32-bit real kind.
Generate and return an object of type display_type.
Example Unix compile command via Intel ifort compiler ⛓
3ifort -fpp -standard-semantics -O3 -Wl,-rpath,../../../lib -I../../../inc main.F90 ../../../lib/libparamonte* -o main.exe
Example Windows Batch compile command via Intel ifort compiler ⛓
2set PATH=..\..\..\lib;%PATH%
3ifort /fpp /standard-semantics /O3 /I:..\..\..\include main.F90 ..\..\..\lib\libparamonte*.lib /exe:main.exe
Example Unix / MinGW compile command via GNU gfortran compiler ⛓
3gfortran -cpp -ffree-line-length-none -O3 -Wl,-rpath,../../../lib -I../../../inc main.F90 ../../../lib/libparamonte* -o main.exe
Example output ⛓
9+2.00000000,
+4.00000000,
-2.00000000,
+6.00000000,
+7.00000000
11+0.964027584,
+0.999329329,
-0.964027584,
+0.999987721,
+0.999998331
13+0.964027643,
+0.999329329,
-0.964027584,
+0.999987721,
+0.999998331
15+0.982013822,
+0.999664664,
+0.179862082E-1,
+0.999993861,
+0.999999166
Postprocessing of the example output ⛓
5examname = os.path.basename(os.getcwd())
9import matplotlib.pyplot
as plt
15df = pd.read_csv(examname +
".csv", delimiter =
",")
17fig = plt.figure(figsize = 1.25 * np.array([6.4, 4.8]), dpi = 200)
20plt.plot( df.values[:, 1]
25for colname
in df.columns[1:]:
26 plt.plot( df.values[:, 0]
33for colname
in list(df.columns[1:]): labels.append(colname)
40ax.set_xlabel(df.columns[1], fontsize = fontsize)
41ax.set_ylabel(df.columns[0], fontsize = fontsize)
43plt.grid(visible =
True, which =
"both", axis =
"both", color =
"0.85", linestyle =
"-")
44ax.tick_params(axis =
"y", which =
"minor")
45ax.tick_params(axis =
"x", which =
"minor")
46plt.xticks(fontsize = fontsize)
47plt.yticks(fontsize = fontsize)
50plt.savefig(examname +
".png")
Visualization of the example output ⛓
- Test:
- test_pm_mathFisher
Final Remarks ⛓
If you believe this algorithm or its documentation can be improved, we appreciate your contribution and help to edit this page's documentation and source file on GitHub.
For details on the naming abbreviations, see this page.
For details on the naming conventions, see this page.
This software is distributed under the MIT license with additional terms outlined below.
-
If you use any parts or concepts from this library to any extent, please acknowledge the usage by citing the relevant publications of the ParaMonte library.
-
If you regenerate any parts/ideas from this library in a programming environment other than those currently supported by this ParaMonte library (i.e., other than C, C++, Fortran, MATLAB, Python, R), please also ask the end users to cite this original ParaMonte library.
This software is available to the public under a highly permissive license.
Help us justify its continued development and maintenance by acknowledging its benefit to society, distributing it, and contributing to it.
- Copyright
- Computational Data Science Lab
- Author:
- Amir Shahmoradi, April 23, 2017, 1:36 AM, Institute for Computational Engineering and Sciences (ICES), University of Texas at Austin
Definition at line 335 of file pm_mathFisher.F90.