|
ParaMonte Fortran 2.0.0
Parallel Monte Carlo and Machine Learning Library
See the latest version documentation. |
|
ParaMonte Fortran 2.0.0
Parallel Monte Carlo and Machine Learning Library
See the latest version documentation. |
Generate and return the unnormalized cumulative distribution function (UCDF) of the Band spectral model/distribution.
More...
Generate and return the unnormalized cumulative distribution function (UCDF) of the Band spectral model/distribution.
See the documentation of pm_distBand for more information on the Band distribution.
The UCDF of the Band model is the integral of its UDF over a range \((\ms{lb}, \ms{ub})\) written as,
\begin{equation} \large \ms{UCDF}_\ms{BAND} = \int_{\ms{lb}}^{\ms{ub}} f_{\ms{BAND}}(E | \alpha, \beta, \ebreak) dE ~. \end{equation}
where \(f_{\ms{BAND}}\) is the UDF of the Band distribution.
While the integration domain should be ideally \([0, +\infty)\), the arbitrary values of \(\alpha\) and \(\beta\) require finite bounds for the integral to be specified by user to ensure convergence.
| [out] | ucdf | : The output scalar or array of the same shape as any input array-like argument, of type real of kind any supported by the processor (e.g., RK, RK32, RK64, or RK128) as the input argument ucdf, containing the distribution UCDF. |
| [in] | lb | : The input positive scalar or array of the same shape as any input array-like argument, of the same type and kind as the input argument ucdf, representing the lower bound of the Band distribution. |
| [in] | ub | : The input positive scalar or array of the same shape as any input array-like argument, of the same type and kind as the input argument ucdf, representing the upper bound of the Band distribution. |
| [in] | alpha | : The input scalar or array of the same shape as other array-like arguments of the same type and kind as ucdf, containing the first shape parameter of the distribution. |
| [in] | beta | : The input scalar or array of the same shape as other array-like arguments of the same type and kind as ucdf, containing the second shape parameter of the distribution. |
| [in] | ebreak | : The input scalar or array of the same shape as other array-like arguments of the same type and kind as ucdf, containing the normalized spectral break energy values: \(\ebreak = \frac{\ebreak}{100\kev}\). |
| [out] | info | : The output scalar of type integer of default kind IK.On output, it is set to positive the number of iterations taken for the series representation of the Gamma function to converge. If the algorithm fails to converge, then info is set to the negative of the number of iterations taken by the algorithm or, to the output error returned by brute force integrator getQuadErr.An negative output value signifies the lack of convergence and failure to compute the UCDF. This is likely to happen if the input value for alpha or beta are too extreme. |
Possible calling interfaces ⛓
0 < lb must hold for the corresponding input arguments.0 < ub must hold for the corresponding input arguments.alpha /= -2 must hold for the corresponding input arguments.0 < ebreak must hold for the corresponding input arguments.0 < invEfold must hold for the corresponding input arguments.beta < alpha must hold for the corresponding input arguments.ebreak = (alpha - beta) * invEfold must hold for the corresponding input arguments.zeta = getZeta(alpha, beta, ebreak) must hold for the corresponding input arguments.CHECK_ENABLED=1.impure.elemental.energy is irrelevant as long as the input values ebreak and zeta are computed in the same physical dimensions and with the same normalizations.
Example usage ⛓
ifort compiler ⛓ ifort compiler ⛓ gfortran compiler ⛓ 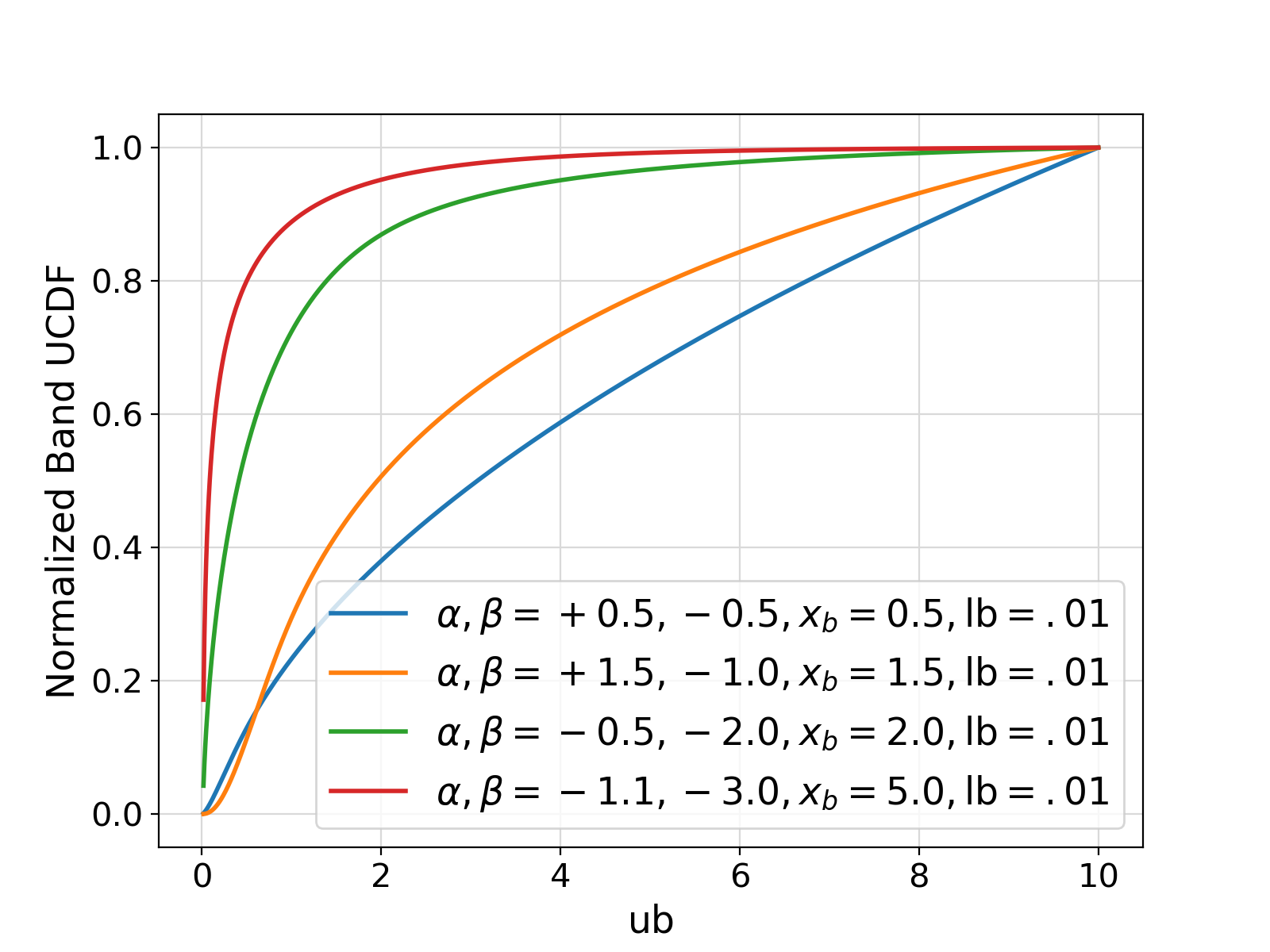
Final Remarks ⛓
If you believe this algorithm or its documentation can be improved, we appreciate your contribution and help to edit this page's documentation and source file on GitHub.
For details on the naming abbreviations, see this page.
For details on the naming conventions, see this page.
This software is distributed under the MIT license with additional terms outlined below.
This software is available to the public under a highly permissive license.
Help us justify its continued development and maintenance by acknowledging its benefit to society, distributing it, and contributing to it.
Definition at line 815 of file pm_distBand.F90.