Introduction
The normal flow of control in procedural programming paradigm is in general, sequential. So is the flow of control in MATLAB.

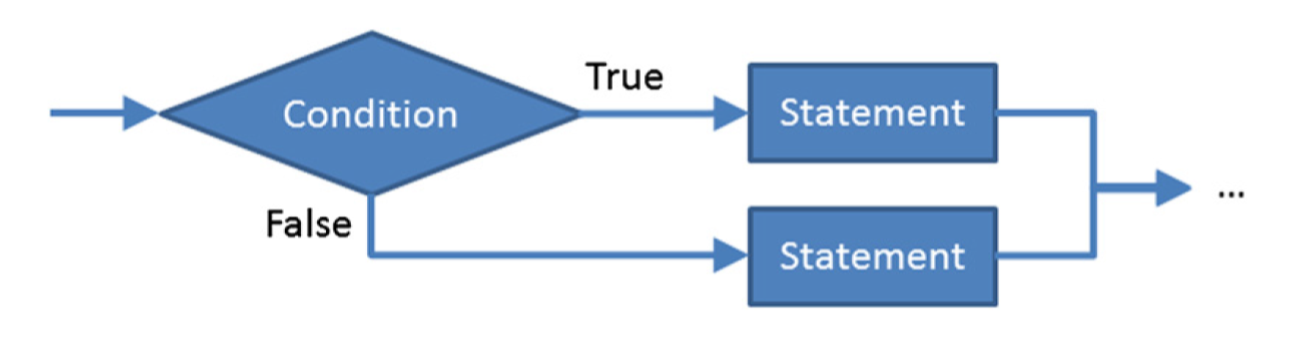
In MATLAB, you can achieve conditional flow control, using either if-block or switch-case.
MATLAB if-blocks
a = input('Enter a number:');
if isnumeric(a) && (a >= 0)
root = sqrt(a);
disp(['Square root(',num2str(a),') = ', num2str(root)]);
elseif isnumeric(a) && (a < 0)
disp(['The input number is negative, there is no square root.']);
else
disp(['Please enter a real number!']);
end
Enter a number:13
Square root = 3.6056
Enter a number:-11
The input number is negative, there is no square root
Enter a number:i
Square root = 0.70711+0.70711i
Note in the above example, how MATLAB treats complex variables. More information on operators that can be used to construct or combine logical conditions for if-statements can be found here.
Exercise
1. Write a MATLAB script that takes two predefined matrices A and B as input and determines whether they have equal size. If so, then it concatenates the two matrices in a column-wise manner.
answer
if isequal(size(A),size(B))
C = [A; B];
else
disp('A and B are not the same size.')
C = [];
end
2. Write a script that checks if it (the script itself) exists!
answer
if exist('myScript.m','file')
disp('Your file exists! Did you expect otherwise?')
else
disp('Your file does not exist! Then perhaps you don''t exist either??')
end
3. Write a script that takes an input predefined number x and calculates the following function,
y={x−1≤x≤1x2otherwiseanswer
x = input('input the value of x: ')
if x >= -1 && x <= 1
y = x
else
y = x^2
end
disp(['y(x=',num2str(x),') = ',num2str(y)])
MATLAB switch-case
Sometimes we may have many if statements which all use conditions based on the same variable. It is not incorrect to use if statements in such cases, but it can lead to a large number of consecutive if statements in our code, making it harder to read and more prone to errors. In this case, it is preferable to use a switch statement. The switch statement offers an easy way of writing code where the same variable needs to be checked against a number of different values.
day = input('Enter a day number:');
switch day
case 1
day_name = 'Monday';
case 2
day_name = 'Tuesday';
case 3
day_name = 'Wednesday';
case 4
day_name = 'Thursday';
case 5
day_name = 'Friday';
case 6
day_name = 'Saturday';
case 7
day_name = 'Sunday';
otherwise
day_name = 'Unknown';
end
disp(['The corresponding weekday is ',day_name,'.'])
Enter a day number:4
The corresponding weekday is Thursday.
MATLAB will compare the switch expression (in this case, day) with each case expression in turn (the numbers 1–7). When a comparison evaluates to true, MATLAB executes the corresponding statements and then exits the switch statement, i.e. control flow passes to after the end statement. The otherwise block is optional and executes only when no comparison evaluates to true. Note that the switch statement is used only for equality tests – we cannot use it for other types of comparison (e.g. >, <, etc.).
A switch statement may also take a cell array as one of its cases,
day = input('Enter a day number:');
switch day
case {1,2,3,4,5}
day_name = 'Weekday';
case {6,7}
day_name = 'Weekend';
otherwise
day_name = 'Unknown';
end
disp(['The input day number corresponds to ',day_name,'.'])
Enter a day number:6
The input day number corresponds to Weekend.
Non-boolean conditions in if-statements
There is a rather interesting feature of conditions for if-statements in MATLAB (also in Python language), that allows the programmer to use a non-boolean variable or non-boolean value type directly in place of the condition in if-statement. What really happens here is that, MATLAB interpreter converts the non-boolean type to a boolean value, when it occurs in place of an if-statement condition.
if 5.6
disp('The condition in this if statement is automatically converted from float to boolean')
end
The condition in this if statement is automatically converted from float to boolean
if ~0.0
disp('A float value of zero is converted to false')
end
A float value of zero is converted to false
if 0.0
disp('A float value of zero is converted to false')
end
if 0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001
disp('Any non-zero float value of any precision is converted to true')
end
Any non-zero float value of any precision is converted to true
if 1.e-323
disp('Any non-zero float value of any precision is converted to true')
end
Any non-zero float value of any precision is converted to true
if 1.e-324 % make sure you don't go beyond computer precision
disp('Any non-zero float value smaller than the computer precision will be set to 0')
end
if ~1.e-324 % make sure you don't go beyond computer precision
disp('Any non-zero float value smaller than the computer precision will be set to 0')
end
Any non-zero float value smaller than the computer precision will be set to 0
if 12
disp('The same rules also hold for integers.')
end
The same rules also hold for integers.
if ''
disp('An empty string is always converted to boolean false, because it is considered an empty logical vector.')
end
if ''
else
disp('An empty string is always converted to boolean false, because it is considered an empty logical vector.')
end
An empty string is always converted to boolean false, because it is considered an empty logical vector.
if []
else
disp('An empty vector is always converted to boolean false, because it is considered an empty logical vector.')
end
An empty vector is always converted to boolean false, because it is considered an empty logical vector.
But note that conversion from cell to logical is not possible in MATLAB:
if {}
disp('An empty cell cannot be converted to boolean value, because MATLAB wants it that way!')
end
Conversion to logical from cell is not possible.
if ['amir']
disp('A non-empty vector is converted to boolean true.')
end
A non-empty vector is converted to boolean true.
if ' '
disp('A non-empty string is converted to boolean true.')
end
A non-empty string is converted to boolean true.
MATLAB’s built-in logical functions
MATLAB has a wide range of functions whose names begins with is, and their output is a logical value type, which can be used in if-blocks. These functions are extremely useful in MATLAB coding, and you will encounter them frequently in your computational life. Here is a rather comprehensive list of them,
| Expression | Description |
|---|---|
isa() | Detect object of given MATLAB class or Java® class |
isappdata() | Determine if object has specific application-defined data |
isbetween() | Array elements occurring within date and time interval |
iscalendarduration() | Determine if input is duration array |
iscategorical() | Determine whether input is categorical array |
iscategory() | Test for categorical array categories |
iscell() | Determine if input is cell array |
iscellstr() | Determine if input is cell array of strings |
ischar() | Determine if input is character array |
iscolumn() | Determine whether input is column vector |
iscom() | Determine if input is Component Object Model (COM) object |
isdatetime() | Determine if input is datetime array |
isdir() | Determine if input is folder |
isdst() | Datetime values occurring during daylight saving time |
isduration() | Determine if input is duration array |
isempty() | Determine if input is empty array |
isequal() | Determine if arrays are numerically equal |
isequaln() | Determine if arrays are numerically equal, treating NaNs as equal |
isevent() | Determine if input is Component Object Model (COM) object event |
isfield() | Determine if input is MATLAB structure array field |
isfinite() | Detect finite elements of array |
isfloat() | Determine if input is floating-point array |
ishandle() | Detect valid graphics object handles |
ishold() | Determine if graphics hold state is on |
isinf() | Detect infinite elements of array |
isinteger() | Determine if input is integer array |
isinterface() | Determine if input is Component Object Model (COM) interface |
isjava() | Determine if input is Java object |
iskeyword() | Determine if input is MATLAB keyword |
isletter() | Detect elements that are alphabetic letters |
islogical() | Determine if input is logical array |
ismac() | Determine if running MATLAB for Macintosh OS X platform |
ismatrix() | Determine whether input is matrix |
ismember() | Detect members of specific set |
ismethod() | Determine if input is object method |
ismissing() | Find table elements with missing values |
isnan() | Detect elements of array that are not a number (NaN) |
isnumeric() | Determine if input is numeric array |
isobject() | Determine if input is MATLAB object |
isordinal() | Determine whether input is ordinal categorical array |
ispc() | Determine if running MATLAB for PC (Windows®) platform |
isprime() | Detect prime elements of array |
isprop() | Determine if input is object property |
isprotected() | Determine whether categories of categorical array are protected |
isreal() | Determine if all array elements are real numbers |
isrow() | Determine whether input is row vector |
isscalar() | Determine if input is scalar |
issorted() | Determine if set elements are in sorted order |
isspace() | Detect space characters in array |
issparse() | Determine if input is sparse array |
isstrprop() | Determine if string is of specified category |
isstruct() | Determine if input is MATLAB structure array |
isstudent() | Determine if Student Version of MATLAB |
istable() | Determine whether input is table |
isundefined() | Find undefined elements in categorical array |
isunix() | Determine if running MATLAB for UNIX®[a] platform. |
isvarname() | Determine if input is valid variable name |
isvector() | Determine if input is vector |
isweekend() | Datetime values occurring during weekend |
For more information on each individual function, see MATLAB’s use manual.